Improving Customs Transit Systems
In the Islamic Countries
81
3
Analysis of the OIC Member States related to CTR
3.1
Current status of the OIC Member States related the CTR
6 OIC MS responded to the survey. The survey responses provide details on the characteristics
of CTR in the countries.
3.1.1.1
CTR Legal Framework
In addition to national customs law, the CAs of OIC MS mostly defines transit regime through
administrative instruction, implementing regulations and standard operating procedures, while
only one MS has a transit policy
(Table 4).
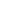
Table 4: Statutory instruments related to customs transit
Frequency
Percent
Customs Transit Policy
1
16.7%
Transit Administrative Instruction
5
83.3%
Implementing regulations
5
83.3%
Standard Operational Procedures
4
66.7%
Total
15
250.0%
Source: Authors’ own compilation
All of the CAs has the authority to conclude administrative agreements or MoUs with the
business community and OGAs
(Table 5). Also, most of them (83.3%) have authority to conclude
such agreements with other CAs, national organizations or associations, port authorities, airline,
and railway companies and express courier services.
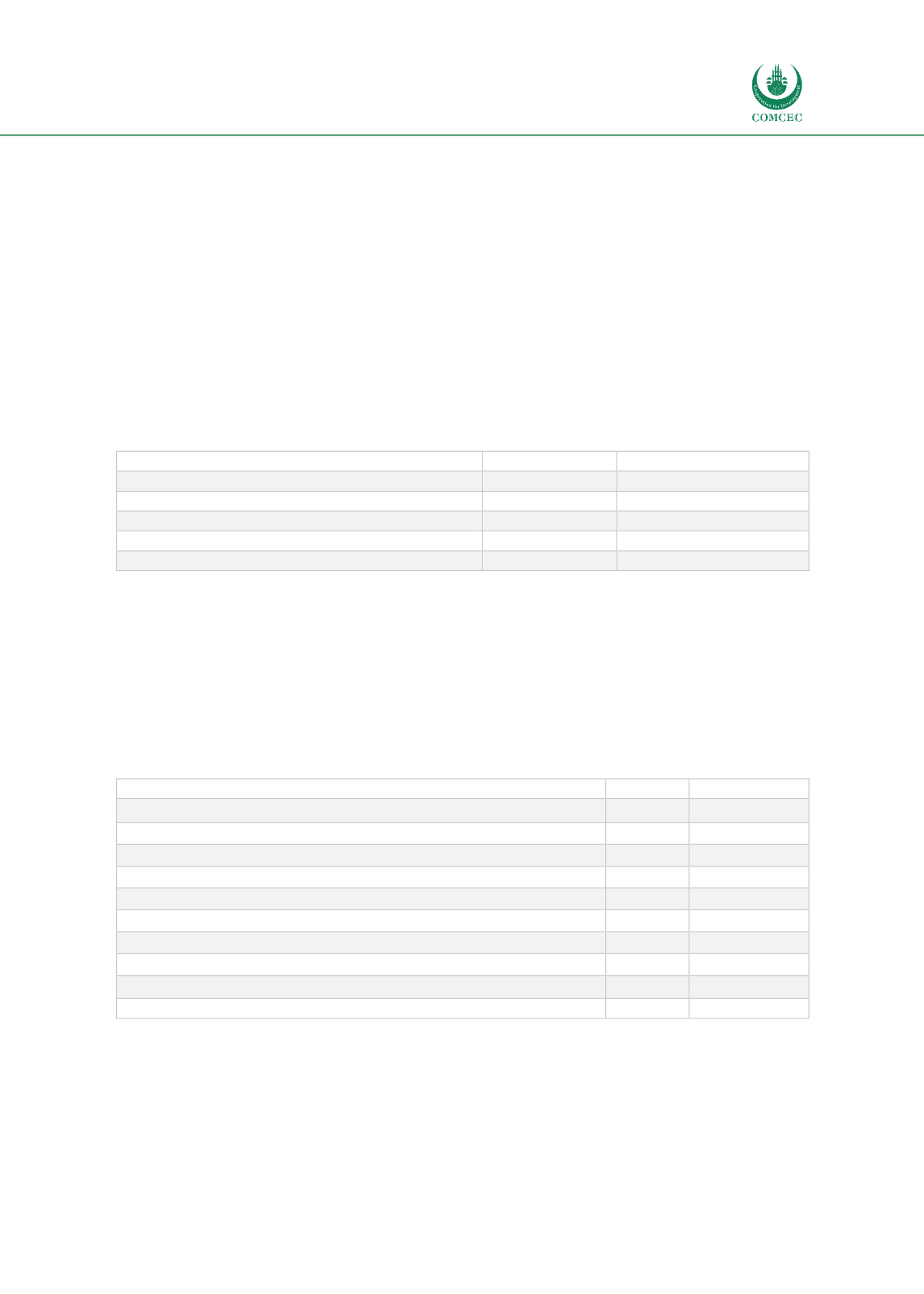
Table 5: Authority to conclude administrative agreements / Memorandum of Understanding
(MoU) related to transit procedure
N
Percent
Other Customs Administrations
5
83.3%
Domestic Trade/business community
6
100.0%
Other domestic government agencies
6
100.0%
Regional/international organizations or associations
4
66.7%
National organisations or Associations
5
83.3%
Port Authorities
5
83.3%
Airlines Companies
5
83.3%
Railway Companies
5
83.3%
Express Courier Services
5
83.3%
Total
46
766.7%
Source: Authors’ own compilation
Regarding membership in international nongovernmental organizations with their existing
roles in CTRs, 5 MS OIC MS have implemented the IRU concept in road transport, while others
are less used
(Table 6).