Strengthening the Compliance of the OIC Member States
to International Standards
103
the body responsible for issuing Senegalese standards. The ASN is funded largely by government, but
also by the sale of standards, training, and other sources. The organization is Senegal’s National Enquiry
Point under the WTO TBT Agreement, while an agency of the Ministry of Agriculture has been
designated to play that role under the SPS Agreement.
Up to the present time, standardization has been gathering momentum in Senegal, but the total number
of standards issued is still relatively small by international standards, totaling 444 (Table 2). Of those,
144 are in the agricultural sector—a key part of the national economy, and a sector seen as having
considerable export potential provided that issues such as quality and consistency can be dealt with. In
all, ASN has 13 technical committees—a relatively small number, but in keeping with the agency’s
limited resources.
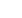
Table 4: Sectoral distribution of ASN standards
Source: ASN
Of ASN’s 444 standards, only 32 are mandatory. The rest are voluntary. This approach is in keeping with
the global trend towards voluntary standards, and indicates that despite the difficulties it faces, ASN is
making a serious effort to support Senegalese primary and secondary industries by putting in place a
modern standards system as part of broader efforts to develop quality infrastructure. However, private
sector take up of standards is an issue. Although mandatory standards are relatively widely used
Sector
Number of standards
Electrotechnical
30
Construction
83
Agriculture
144
Environment
89
Commerce
4
Chemical
51
Solar energy
19
Household energy
5
Health
19