Preferential Trade Agreements and Trade Liberalization Efforts in the OIC Member States
With Special Emphasis on the TPS-OIC
128
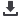
Figure 49:
Concentration of Exports to the GCC, 2000-12 (higher values indicate more
concentrated trade)
Calculations based Comtrade data
SAARC
The South Asia Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA) was signed in January 2004 and entered into force
on 1 January 2006 with implementation starting from mid-2006. Parties to the agreement
include four OIC members: Afghanistan (since 2011), Pakistan, Bangladesh, Maldives and four
other regional partners: India, Sri Lanka, Nepal, and Bhutan. These countries are members of
the South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation (SAARC) that has a much broader scope
than just economic and trade issues. Tariff liberalization started in 2006 and the agreement
foresees different tariff schedules for its members classified as least- developed countries
(LDC) and for non-LDC countries. There are also country-specific lists of sensitive products
that are excluded from tariff liberalisation but are reviewed periodically with a view of gradual
removal of products from the list. At the end of 2011 the numbers of products in the sensitive
lists were as follows: Afghanistan (858), Bangladesh (987), Bhutan (150), India (25), Maldives
(277), Nepal (998), Pakistan (936) and Sri Lanka (845) (WTO, 2012a).
Under SAFTA tariffs applied by LDC members are to be reduced to by 0-5% by 2016, while for
non-LDC members the deadline for reducing tariffs on LDC’s imports was 2009 (WTO, 2012a).
It is difficult to assess the overall progress in tariff liberalisation. Data reported in WTO et al
(2013) suggests a mixed picture. As of 2011 Bangladesh reportedly benefited from meaningful
preference margins in India (13.7 percentage points - trade weighted), although the number of
products exported to India was actually very limited (WTO et al, 2013). Pakistan reduced and
capped all its tariffs on imports from Bangladesh at 5% and Sri Lanka lowered tariffs to the
range of 0-5%. At the same time Pakistan, by far the most important export partner of