Special Economic Zones in the OIC Region:
Learning from Experience
42
4.2.1
Spatial Characteristics
Connectivity and access are considered to be key to the success of economic zones. In order to
be physically and economically linked to both domestic and international markets, proximity to
major transport and logistics infrastructure is important.
Size of Zones
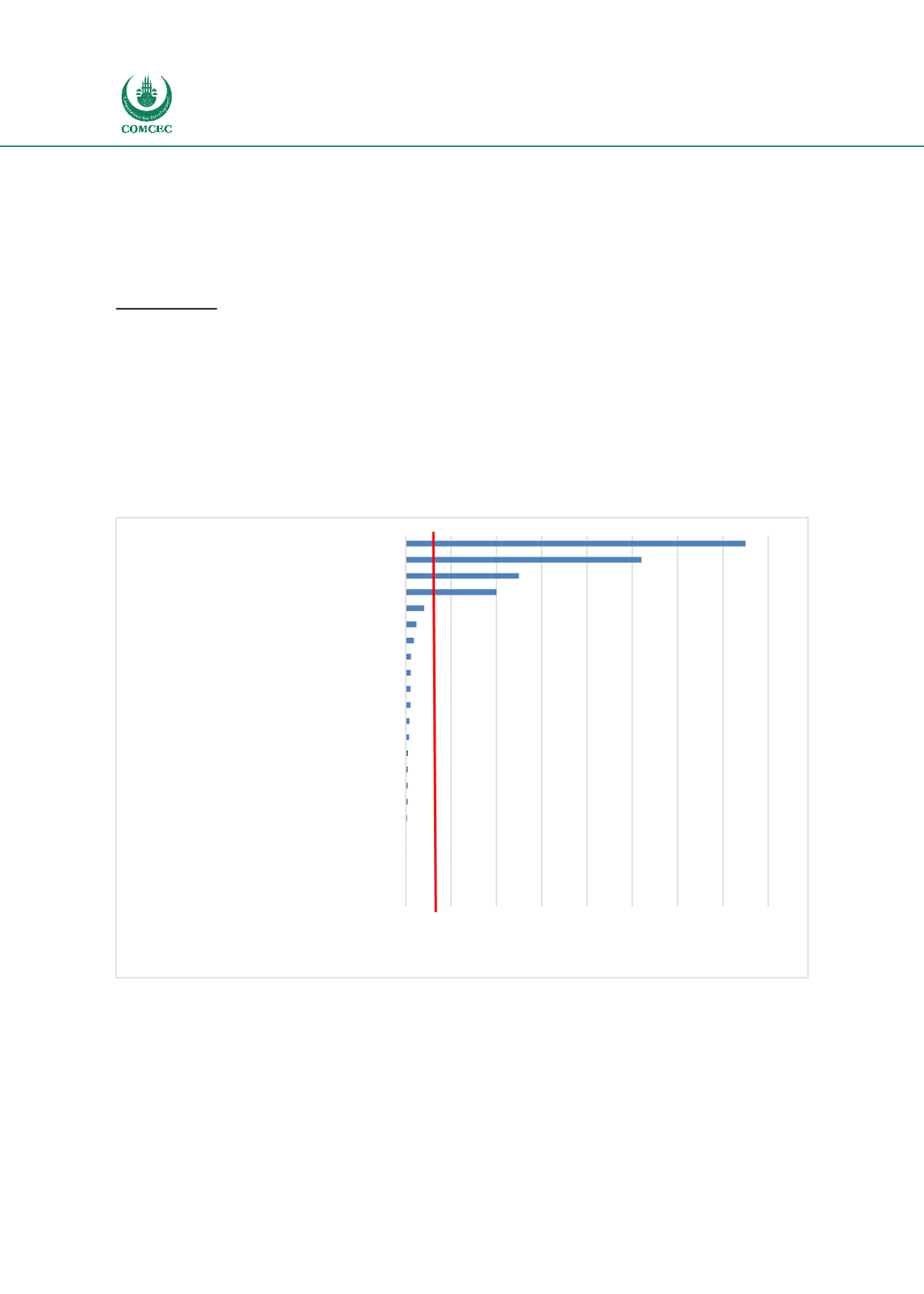
Analysis of the selected SEZs indicates that the average size of economic zones within OIC
Member Countries varies between 12ha to 37,500ha. The average size of zones was recorded as
approximately 4,100ha. This is representative of the broad nature of the selected zones as well
as the activities located within them and their industrial focus. The smaller zones tend to be
focused on the service sector and high value manufacturing and industrial activities which the
largest zones are focussed on export processing, industrial, energy and petrochemical activities.
Figure 4 - Size of Selected SEZs within OIC Member Countries
Source: BuroHappold Analysis 2017
When looking at size of zones by typologies it can be observed that the largest zones, particularly
those over 10,000 hectares are Freeports, SEZs and FTZs, whilst EPZs within OIC Member
Countries are observed to be smaller; between 12 hectares and 2,000 hectares.
0 5,000 10,00015,
00020,00025,00030
,00035,00040,000
King Hussein Business Park
Suez Trade Free Zone
Antalya Free Zone
Nasr City Public Free Zone
Mersin Free Zone
Midparc
Kenitra Automotive Free Zone (Atlantic Free Zone)
North Sitra Industrial Estate
Ras Al Khaimah Free Trade Zone
Bahrain International Investment Park
Tanger Med Free Trade Zone
Port Klang Free zone
Bayan Lepas Free Industrial Zone
Bitung
MBTK
Alexandria Public Free Trade Zone
Ma'an Development Area (MDA)
Lekki Free Zone
Tanjung Api-Api
Ogun Guandong Free Trade Zone
Jebel Ali Free Zone (JAFZA)
Iskandar
Aqaba Free Zone
Hectares
Average - ~4,100ha