Facilitating Smallholder Farmers’ Market Access
In the OIC Member Countries
61
government can implement sound policies that promote private sector development.
Government effectiveness relates to perceptions about the government’s ability to deliver
public services and formulate and execute sound policies. Fiduciary stewardship captures
perceptions about the government’s ability to control grand and petty corruption and to
block efforts to use public position for private gain.
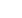
As the figure shows, Bangladesh lags behind most of the 218 countries covered by the
Worldwide Governance Indicators. Ranking for fiduciary stewardship has demonstrated
significant improvement and rankings for voice and accountability and the regulatory
quality have also shown some positive dynamics. With this being said, the country’s
ranking on rule of law and, especially, government effectiveness fell between 2002 and
2012.
The Cost of Doing Business study
120
reports on a separate set of perceptions about the
strength of the Bangladesh institutions put in place to support the business environment.
The indicators are constructed from business surveys, focusing on business regulations.
Overall, Bangledesh ranks 130
th
out of 189 countries covered by the surveys. When asked
about how well laws and regulations protect investors, Bangladesh does well, ranking in
the top 12% of surveyed countries. However does especially poorly when respondents are
asked about contract enforcement.
While agriculture’s share in the overall economy is diminishing, agriculture retains
considerable importance in Bangladesh’s rural economy, as indicated by its prominence in
the government’s key strategy documents. Agriculture is a central component of the
inclusive growth strategy advocated in the Perspective Plan and of the national food
security agenda.
121
The National Food Policy identifies 26 specific Points of Action focusing
on food supply, food access, and food utilization, especially for women and children. The
Country Investment Plan secures and allocates the budget to implement the National Food
Policy and its Plan of Action.
122
The agricultural sector and rural economy also feature
strongly in the national food security strategy framework, which emphasizes efforts to
enhance research and extension, improve input markets, improve market access, and
reduce marketing and storage costs.
Historically, national policies and strategies to achieve food security have been dominated
by initiatives to increase food grain (principally rice) production. The inward-looking,
interventionist sectoral framework and restrictive trade policy framework that prevailed
at independence in the early 1970s were eventually followed by significant reforms in the
1980s and especially the 1990s. While areas for further reform remain, the current policy
context is characterized by a stable macro framework, significantly reduced price
distortions, a more liberalized and outward-oriented trade regime, and an emphasis on
the private sector as the engine of economic growth.
123
120
World Bank (2013b).
121
World Bank (2013e).
122
Ministry of Food and Disaster Management (2011).
123
World Bank (2013e).