Facilitating Smallholder Farmers’ Market Access
In the OIC Member Countries
90
Kyrgyz agriculture is driven by smallholder farmers that are relatively new to farming.
Following the collapse of Soviet Union, agricultural land was transferred to private
ownership in three phases. First, in 1991–93 legal ownership changed from state property
to private ownership. Second, between 1994 and 2004, 75 percent of the country’s 1.2
million hectares of arable land was shifted from corporate to individual holdings,
144
and
the moratorium on sales of agricultural land was lifted. Third, since 2004 the physical land
transfer has been finalized. New individually held farms have received support, and
enabling market conditions have been created.
Seventy-eight percent of arable land (940,000 hectares) went to private (peasant) farms.
Farm size ranges from 0.2 hectares to 2.9 hectares; 96 percent of private farms are smaller
than 2 hectares
(Figure 56). Most of the national livestock herd is owned by family-based
private farms. Household farms (garden plots) occupy around 96,700 hectares (8 percent
of agricultural land); the average size of a household farm is 0.10 hectares. In addition,
some 172,300 hectares of agricultural land (14 percent) are farmed by agricultural
enterprises that include state and collective farms. About 75 percent of the country’s
arable land is irrigated.
144
The remaining areas were kept in the Land Distribution Fund.
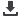
FIGURE 55: STRUCTURAL CHANGE AND THE KYRGYZ REPUBLIC ECONOMY, 1985–
2011
Source:
World Development Indicators (World Bank 2014h).