Improving Agricultural Market Performance
:
Creation and Development of Market Institutions
86
4.2 Agricultural Lending
Lack of access to finance is an important constraint to improvement of agricultural
productivity and production, which especially affects smallholders. Lacking adequate finance,
small producers cannot invest in better seed varieties, fertilizers and other inputs, or post-
harvest handling techniques that increase value. Without finance, they cannot increase the
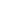
amount of land they cultivate. Agricultural finance entails risks specific to each stage of the
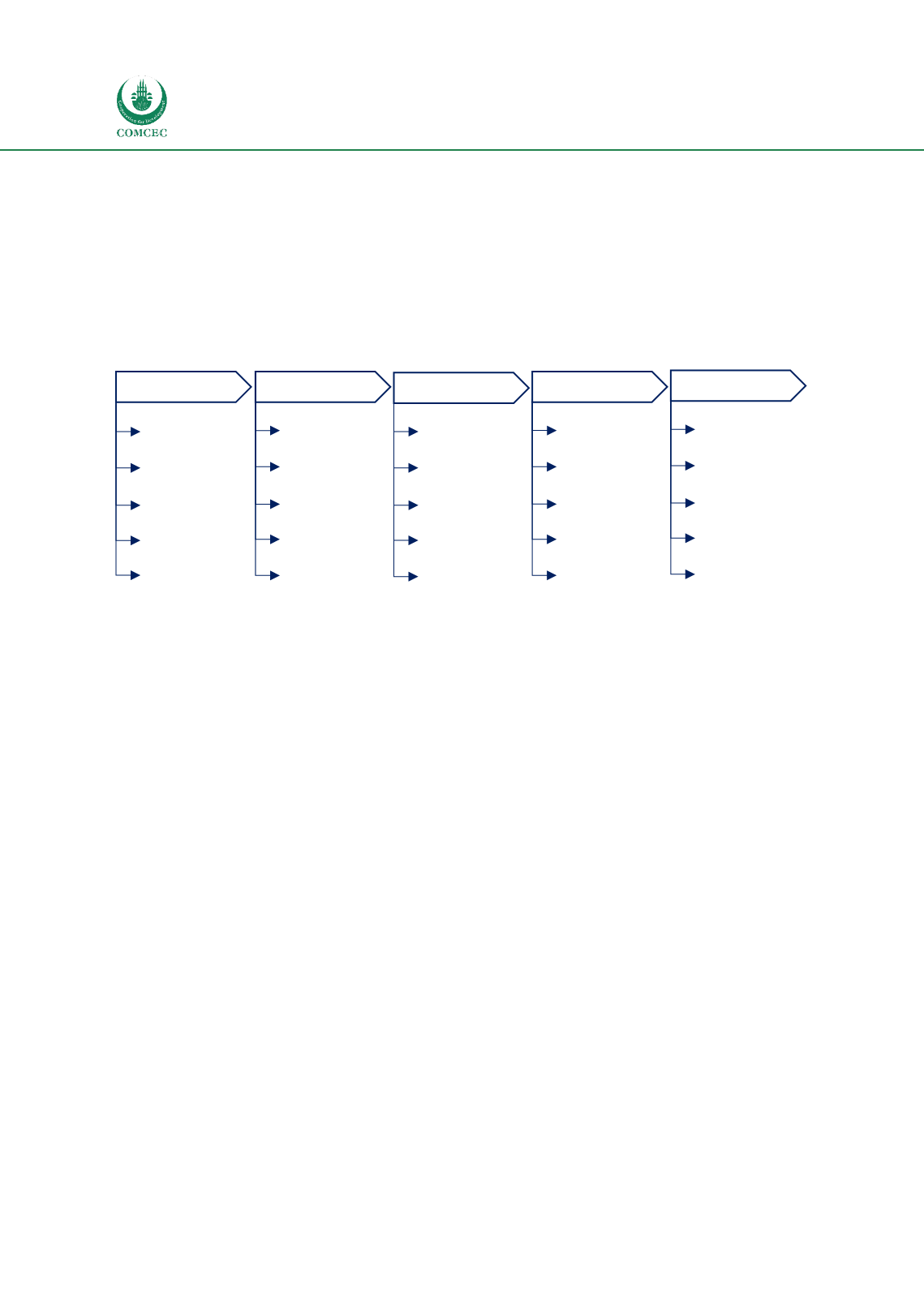
value chain, as illustrated i
n Figure 4 .Figure 4 – Risks along the agricultural value chain
Source: Investment Consulting Associates – ICA (2017), based on IFC (2015)
Financial institutions, agricultural lending programs, and other financial intermediation can
help reduce these constraints and improve market performance. One example of an
agricultural lending institution that has succeeded in doing this is the
Nigerian Incentive-
based Risk Sharing System for Agricultural Lending (NIRSAL).
In Nigeria, previous agricultural lending schemes encouraged banks to lend, but lacked a clear
strategy on how to use this activity to fix agricultural market systems and make lending more
effective. The Nigerian Incentive-based Risk Sharing System for Agricultural Lending (NIRSAL),
launched in 2013 as a public-private initiative sponsored by the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN)
was intended to address agriculture market systems together with agricultural financing. The
US$500 million program is based on five pillars that aim to “de-risk” agricultural lending,
lower the cost of lending for banks, and – through both activities – enhance the functioning of
the market.
The funds are divided across the pillars as follows:
1.
Risk-sharing Facility (US$300 million).
Addresses banks’ perception that
agriculture is a high-risk sector, NIRSAL will share their losses on agricultural loans,
up to 50% on larger loans and up to 75% on smaller ones.
2.
Insurance Facility (US$30 million)
. Expands insurance for agricultural lending to
help reduce credit risks and increase lending across the entire market system. This is
intended to attract new private sector insurance providers into the market in
partnership with the National Insurance Commission, to expand existing coverage
offered by the Nigerian Agricultural Insurance Corporation (NAIC), and to pilot and
Producers
Input
Suppliers
Quality
Availability
Infrastructure
Knowledge
Financing
Price
Production
Organization
Financing
Institutional
Transporters
Quality control
Infrastructure
Technology
Logistics
Temporary over-
supply
Processors
Regulatory
environment
Technology
Finance & staffing
Product quality
Government
policies
Retailers
Storage
Infrastructure
Price
Lost production
Government
policies