
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
94
primary issuance of securities for monetary policy are deposited in a separate, blocked
account to which the government does not have access (MoFPED 2013).
Debt reporting
Each year, the Minister for Finance, Planning and Economic Development presents to
parliament a report on the state of Ugandan public debt, grants and guarantees that includes a
detailed description of the structure of the debt portfolio (see, for example, MoFPED 2014,
Republic of Uganda 2015, 2016). The debt strategy document also includes statistics and cost
and risk analysis of the existing debt portfolio (MoFPED 2016). Both documents are published
online.
Debt management strategy (incl. risk management)
The objective of the government concerning public debt management is to “meet the
Government’s financing requirements at the minimum cost, subject to a prudent degree of risk,
(…) ensure that the level of public debt remains sustainable, over the medium and longterm
horizon while being mindful of the future generations and (…) promote the development of the
domestic financial markets” (MoFPED 2016, p. 89).
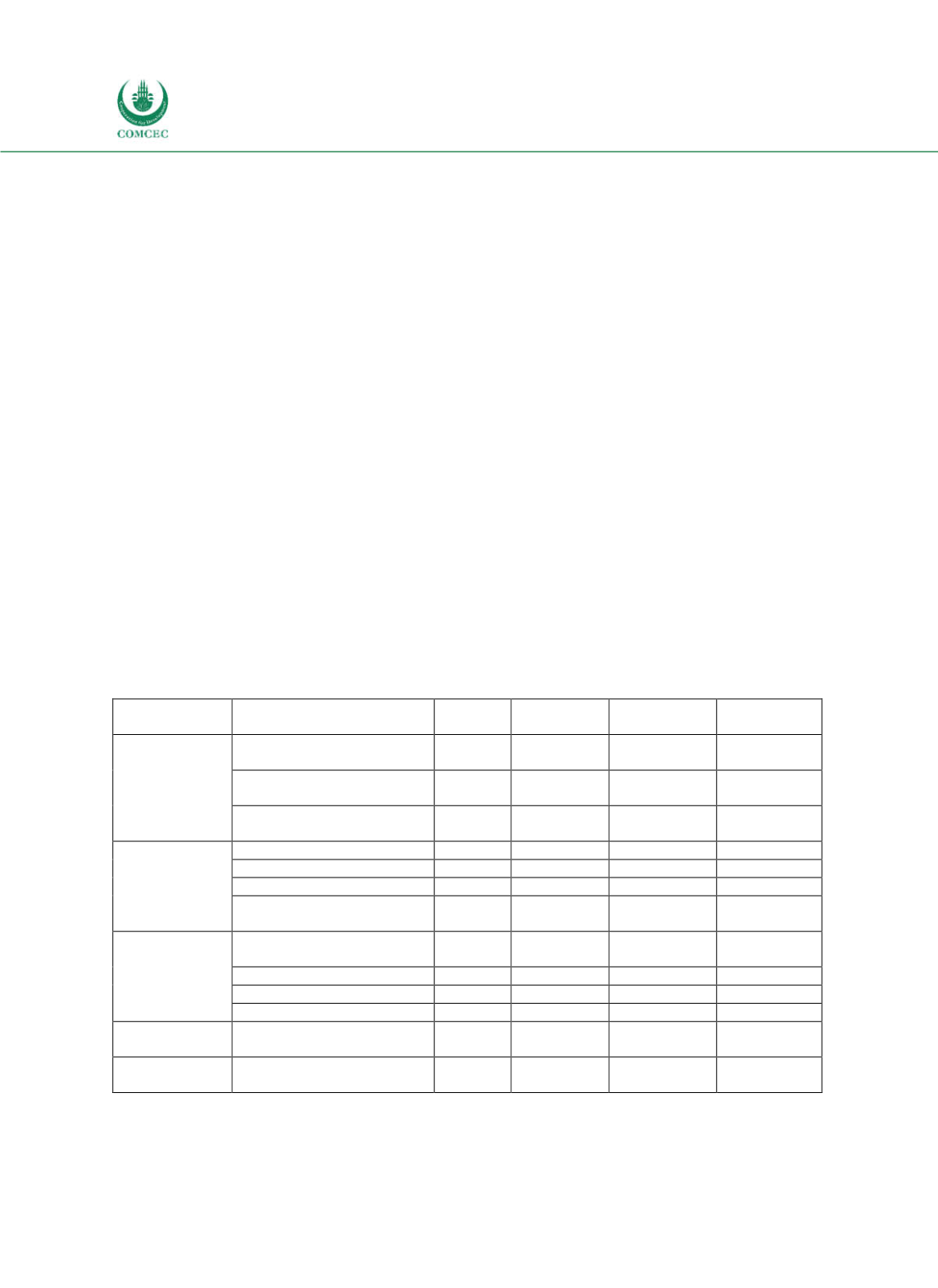
The Public Debt Management Strategy (PDMS) is prepared by the MoFPED in collaboration
with the Bank of Uganda. The government considers prudent public debt management to be an
important policy field as the government’s debt portfolio can have a huge impact on the overall
economy (MoFPED 2016). The PDMS 20162021 includes an assessment of the cost and risk
characteristics of the current debt portfolio and compares the respective indicators with the
benchmark objective values (see Table 44). Finally, it presents the mediumterm guidelines
for public debt management.
Table 4-4: Uganda - Cost and Risk Indicators of the Government’s Debt Portfolio
Type of risk
Risk indicator
June
2015
June 2016
(estimated)
2020
(projections)
Indicative
Constraint
Solvency
PV of debt (% of GDP)
23.6% 27.2% 34.5% Less than
50%
PV of external debt (% of
GDP)
10.3% 16.3%
Less than
30%
PV of domestic debt (% of
GDP)
13.4% 10.9%
Less than
20%
Cost of debt
WAIR (%)
4% 4%
Max. 6%
External debt WAIR (%)
1% 1%
Max. 2%
Domestic debt WAIR (%)
8.3% 8.3%
Max. 16%
Interest payments (% of
GDP)
1.3% 1.2%
2% Less than 2%
Refinancing
risk
Debt maturing in 1 year
(% of total)
22.4% 14.1% 9.3% Max. 15%
ATM external debt (years)
18.7
16.8
13.2
Min. 15years
ATM domestic debt (years)
2.8
3.9
3
Min. 3years
ATM total debt (years)
12.2
11.9
11.3
Min. 3years
Interest rate
risk
ATR (years)
12.2
11.6
11.1
Min. 10years
Exchange rate
risk
FX debt (% of total)
59.2% 62.1% 80.8% Less than
80%
Note: ATM = Average Time to Maturity; ATR = Average Time to Refixing; PV = Present value; FX = Foreign
exchange; ST = Short-term; WAIR = Weighted average interest rate.
Source: MoFPED (2016, p. 24).
















