4
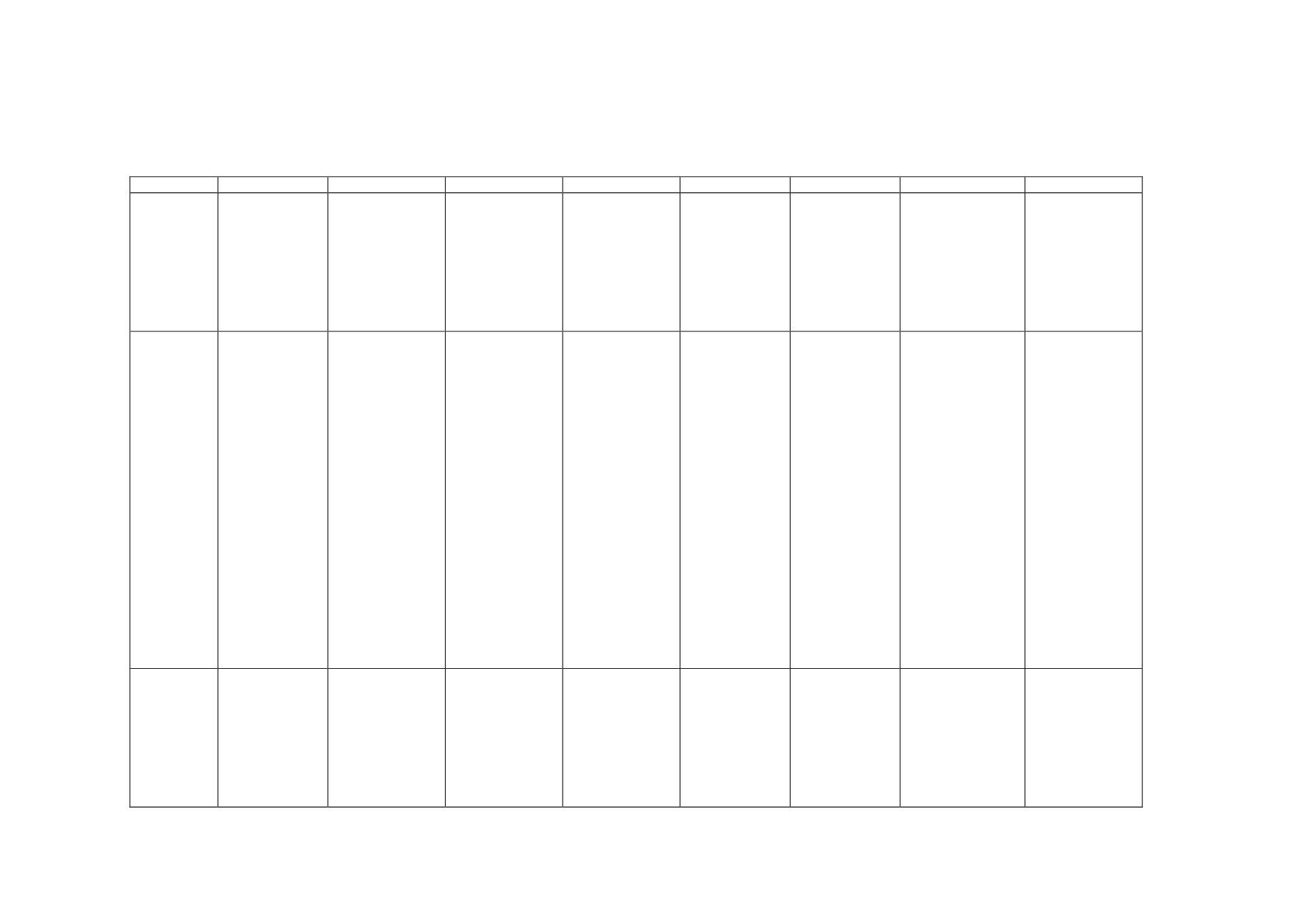
Table 1. Qualitative comparison
Egypt
Indonesia
Ivory Coast
Morocco
Nigeria
Pakistan
Turkey
UAE
Bank
supervision
The Central
Bank of Egypt
(CBE)
Bank Indonesia
(BI) , now moved
to new regulator,
Otoritas Jasa
Keuangan (OJK)
The Central Bank
of West African
States (BCEAO)
The Bank Al-
Maghrib, founded
as the successor
to the Banque
d’Etat du Maroc
The Central
Bank of Nigeria
(CBN)
State Bank of
Pakistan (SBP)]
The independent
Banking
Regulation and
Supervisory
Agency (BRSA) or
Bankacılık
Düzenleme ve
Denetleme
Kurumu (BDDK)
Central Bank of
the UAE
Legal
Regulatory
Framework
The Law of the
Central Bank,
the Banking
Sector and
Money contains
the legal basis
for the
oversight
function of the
Central Bank of
Egypt (CBE).
Central Bank Act,
the UU No.
23/1999 on Bank
Indonesia (17
May 1999), then
amended with UU
No.3/2004 (15
January 2004)
BCEAO Bill No.
15/2002/CM/UE
MOA related to
payment systems
in the WAEMU
space issued on
September 2002.
Under the
banking law, The
Bank Al-Maghrib
and its Governor
are operationally
independent in
making decisions
on banking and
payment
supervision.
CBN Act of 1958
(amended with
CBN Decree No.
24 of 1991),
CBN Decree
Amendments
No. 3 and No. 4
of 1997, No. 37
of 1998, No. 38
of 1998, 1999
and CBN Act of
2007.
The State Bank
of Pakistan is a
central bank
established
under the State
Bank of
Pakistan Act,
1956. Other
companies were
established
under the
Banking
Companies
Ordinance,
1962. The
Financial
Institutions
(Recovery of
Finances)
Ordinance, 2001
provides further
legal structure .
The Central Bank
of the Republic of
Turkey is
responsible for
meeting financial
system stability,
operation,
regulation and
oversight of
payment systems.
The Banking
Regulation and
Supervision
Agency (BRSA),
issues licences,
and supervises
major financial
institutions.
Union Law No. 10
of 1980 regulate
the central bank,
the monetary
system, as well as
organisation of
banking and
payment systems.
Banking
service
provision
There are 5
public sector
banks, 27
private and
joint-venture
banks and eight
branches of
foreign banks
operating in
There are 120
commercial
banks in
Indonesia (four
state-owned
commercial
banks, 79 private
national banks,
26 government
There are more
than 20 banks,
including
international
banks, regional
banks, and
private banks
(2012),
In 2011, there
were 76 financial
institutions,
including 16
commercial
banks, 37
financing
companies, 6
offshore banks,
There are 24
banks operating
in Nigeria.
There also
exists a network
of highly
structured
community,
development
There are 5
public sector
commercial
banks with
2,022 total
branches, 22
local private
banks with
8,388 total
There are 47
banks (13
investment banks,
25 commercial
banks, 4
participation
(Islamic) banks
and 5 branches of
foreign banks)
There are 23
domestic
commercial
banks (three of
which are Islamic
banks), 28
foreign banks
operating in the
UAE, as well as