Improving Transport Project Appraisals
In the Islamic Countries
96
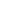
Table 5.2: Studies required by Art. 5 of the By-Law on Implementing the PPP Act, divided per
general item of contents
General item
Studies required by Art. 5 of the By-Law on Implementing the PPP
Act
Project identification
Initial studies
Demand analysis
Feasibility studies
Technical design
Technical studies on first stage
Technical studies on second stage
Land acquiring plan
Machineries, facilities and special materials supply plan
Executive structure
Management- and time
plan
Timing plan (at level zero)
Utilization system and service and maintenance
Financial analysis
Financial plans including balance sheet of income and
expenditure, capital depreciation and investment return, liquidity
flow in development and utilization processes
Economic analysis
Economic justification studies
Environmental analysis
Environmental studies
Risk analysis
Risk assessment studies
Sources: CSIL.
As regards socioeconomic effects considered in transport project appraisal in Iran, the following
items are the ones typically included:
Time saving
;
Safety
78
;
Environmental impacts
(Sea
pollution, Air pollution, Soil pollution, Noise pollution, GHG emissions, Chemical pollution);
Regional and local impacts
;
Social Responsibility
. As obvious, the considered effects may vary
depending on the type of project at stake, in light of the significant differences between transport
modes.
A quantification of the effects is performed, primarily through the unit values provided by the
PBO in its Handbook. However, different practices are in place as regards the effects’
monetisation. CDTIC does attach monetary values to quantities
79
(computing, for example, the
value of accidents, of fuel consumption
80
, and of traffic), using mainly shadow prices. PMO, on
the contrary, does not use shadow prices, nor willingness-to-pay (WTP) approaches, but rather
quantifies the benefits with market prices. The MRUD, furthermore, is reported to make use of
WTP in order to calculate yearly the tolls of freeways.
78
Road safety, especially in metropolitan areas, represents a very significant issue in the country. According to some
estimates, Iran is the first country worldwide in terms of number of road accidents, deaths and injuries per year. Source:
International Business Publications, 2016, p. 58.
79
This practice is particularly followed in the case of Build-Lease-Transfer (BLT) projects.
80
In Iran, the government heavily subsidises fuel. Savings in fuel consumptions, therefore, can be considered to generate
not only environmental benefits, but also financial benefits for the public sector. At a strategic level, the reduction of fuel
subsidies is one of the government’s goals in the medium term.