Islamic Fund Management
123
completed by Law 68-12 enacted in June 2014―as an international business hub and a leading
financial centre in Africa
(www.casablancafinancecity.com). The development of Islamic
finance complements and expands the range of financial products offered, and increases the
attractiveness and dynamism of Casablanca as a leading financial centre in Africa. Casablanca
ranked 32
nd
in the Global Financial Centre Index 2018―and first among the African financial
centres―ahead of Johannesburg (52
nd
) and Mauritius (56
th
) (GFCI 23, 2018). It featured among
the 15 financial centres likely to become more significant in the near future.
Morocco’s financial system is mostly concentrated on the banking sector while capital market
development is still nascent. Its banking system is among the largest in the region, with total
banking assets accounting for about 140% of GDP (IMF, 2016). This explains the country’s
strategy of venturing into Islamic banking first, before considering the development of other
segments of the Islamic financial sector, such as
takaful
and Islamic capital markets.
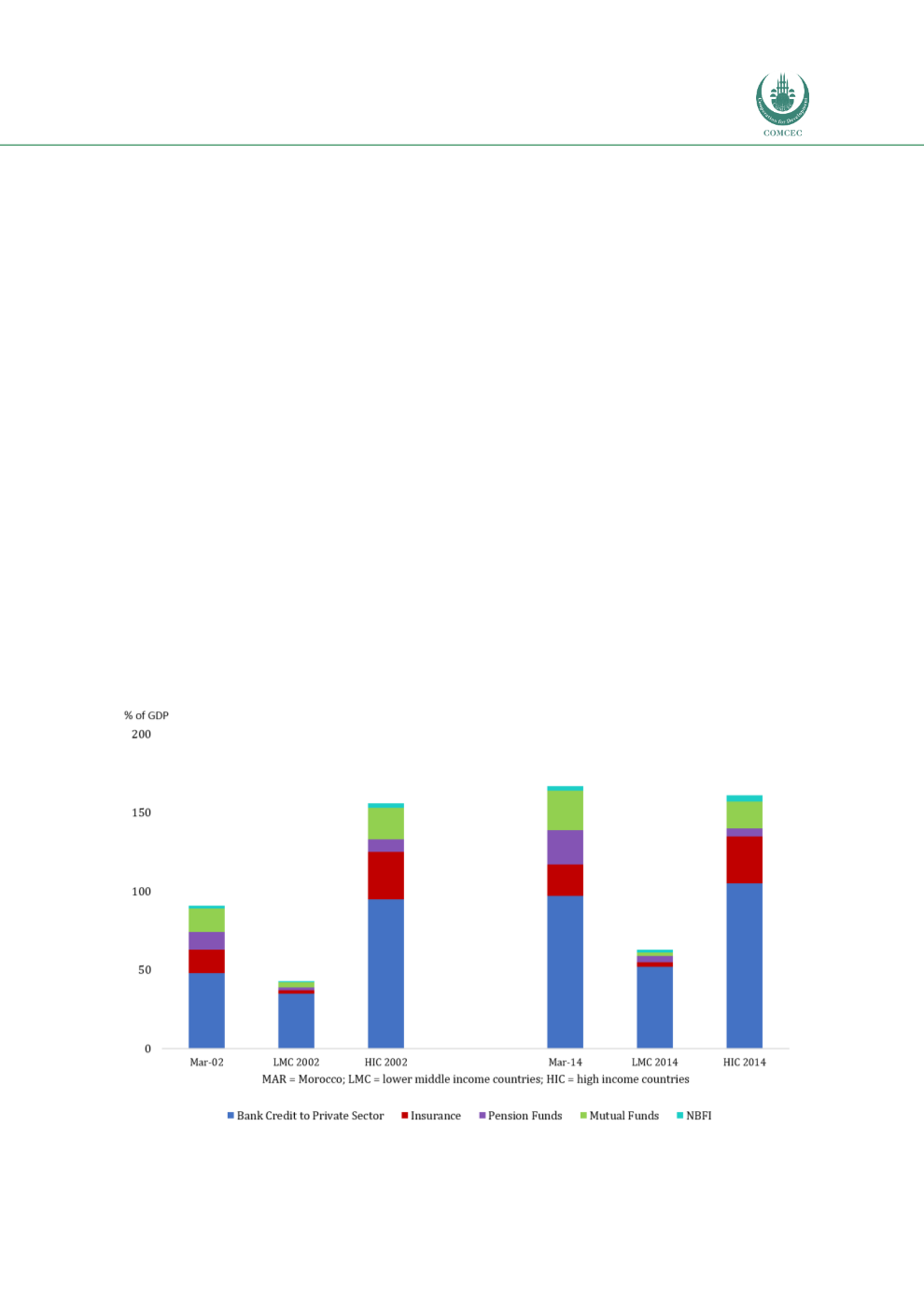
The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Report on Morocco (2016) notes that its financial
system assets (banking, insurance, pension funds, asset management) have reached levels
comparable to high-income countries, as reflected in
Chart 4.17 .The country’s insurance
sector represents 8% of GDP and is inter-connected with the banking and asset management
sectors. The financial system also comprises microcredit associations and finance companies,
the assets of which account for 10.5% of GDP. Morocco started upgrading its legal and
regulatory framework in 2014, with a new banking law enacted the same year, and
independent regulators created for the capital markets (Autorité Marocaine du Marché des
Capitaux, AMMC) and insurance sector (Autorité de Contrôle des Assurances et de la
Prévoyance Sociale, ACAPS). The regulator for the banking sector is Bank Al-Maghrib while the
Ministry of Economy and Finance oversees financial sector policies and development.
Chart 4.17: Assets of Main Intermediaries in Morocco’s Financial System
Source: IMF (2016)