COMCEC Agriculture Outlook 2017
28
When discussing irrigation, it is not sufficient to know only the water potential. Additionally,
we need to look at the utilization of this potential in agriculture. Large part of the OIC member
countries are located in arid and semi-arid regions geographically. Hence, widespread and
modern irrigation systems, including water storage facilities are required.
In the OIC member countries as a whole traditional ways of irrigation are widely used.
Therefore, the efficient use of water in agriculture is not adequately addressed by most of the
countries of the region where sustainability of the existing irrigation systems are at stake.
While surface irrigation is by far the most widely used system in irrigation (practiced on 82.1
percent of the total full and partial controlled irrigation area), the most water-saving system
through micro-irrigation techniques is only practiced on a mere 1.7 percent of the total
irrigation area.
11
2.5.
Fertilizer
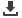
The average use of fertilizer per hectare in the OIC member countries increased from 57
kilograms in 2003 to 70.6 kilograms in 2014. This is far behind of the world average. As of
2014, the world average fertilizer use reached 120 kilograms which was more than 60 percent
higher than the OIC average.
Figure 23. Fertilizer Use in the OIC and World
(2013)
Source: FAOSTAT
At the sub-regional level, the use of fertilizers in the African Group Countries was very low
with 12.3 kg/hectare in 2013. On the other hand, the use of fertilizer in Arab Group Countries
and Asian Group Countries are 78.2 kg/hectare and 112.0 kg/hectare, respectively.
11
SESRIC, 2014
57,0
60,1
62,0
65,7
65,1
66,0
67,2
69,1
71,2
72,0
73,2
70,6
103,3
106,2
104,8
107,8
113,6
108,5
107,4
116,2
120,6
119,4
119,9
119,9
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
kg/ha
OIC
World