75
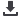
Figure 38: Health expenditures development in Uganda between 2000 and 2016
Source: World Development Indicators
Health data and information management systems in Uganda
The level of access to health information is poorly documented. However, e-health has become a
stronger area of focus, and a national e-health technology framework completed and an e-health
strategy draft. Several local innovation programs on e- and m-health exist and could be leveraged to
build country ownership and reduce the total cost of ownership (Ministry of Health, Uganda, 2015).
However, Information Communication Technology (ICT) is not well developed in Uganda at rates
optimal to match health needs of the poor. On average, only 3.8 per cent of the household heads own
a computer (UBOS, 2018). Also, phone coverage is not wide spread and the poor neither have access
to SMART phones, nor are they likely to be able to afford airtime and internet data to access health
information.
At national level, the country was able to transition to Health Management Information Systems
(HMIS), District Health Information System (DHIS)-2 which is an electronic web-based reporting
mechanism and revised reporting tool availed to ensure disaggregation and Human Resource for
Health Information System (HRIS). The affiliated institutions in collaboration with Ministry of Health,
have some notable eHealth services such as the Ware House Management System (WMS) and the
computerized Logistic Management Information System (LIMS). Others include mTrac, U- Report
(MoH, Uganda, 2016c). The mechanisms for evidence generation and oversight however, need to be
streamlined and strengthened to avoid scenarios where data generation is resource driven as opposed
to need driven (Ministry of Health, Uganda, 2015). Other platforms are mTrack and Uganda EMR.
CDC/PEPFAR utilizes Hibrid for data collection and reporting and has also rolled out Himap in
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1.000
2000
2005
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
2015
2016
Expenditure in million current US$
Government schemes
Voluntary health care payment schemes
Voluntary health insurance schemes
NPISH financing schemes (including development agencies)
Household out-of-pocket payment