
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
55
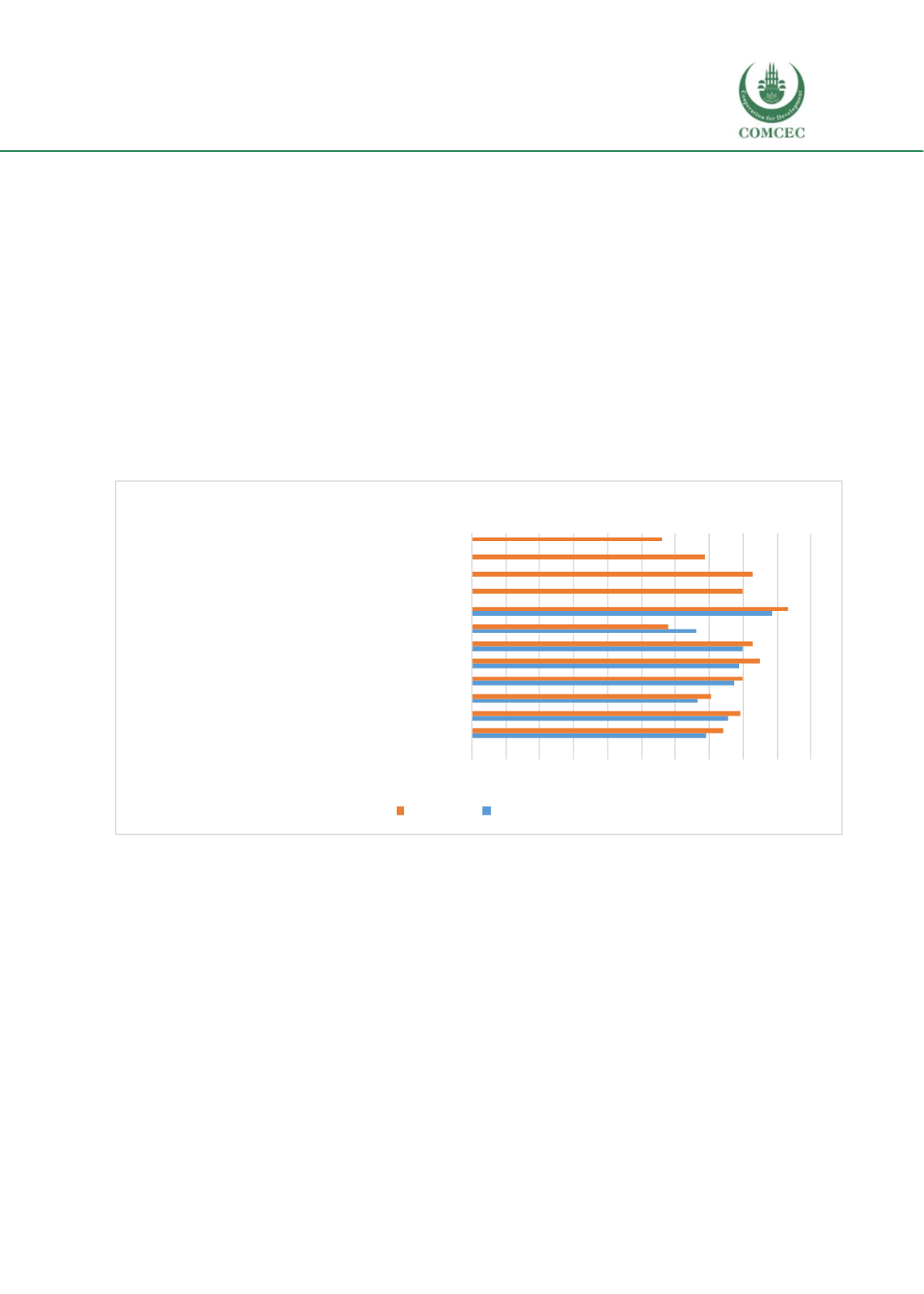
that Bangladesh does not sendmany of their skilled people to foreign country due to English or
other language difficulties. Items 9, 10, 11, and 12 were constructed only for administrators. In
item 9, most of the administrators (80.9% & X=4.00) agreed that Bangladesh does not have
adequate TVET institutions for skill training. Most of the participated administrators (90.5%)
responded (agreed) to the tenth item that there is a lack of competent instructors (teachers) in
TVET sectors. In case of youth opinion, 61.9% of administrators agreed that youth’s opinions
have not been taken into consideration while formulating policies for the development of
vocational education. The mean value, X for A = 3.43, rangeswithin average valuation, which is
slightly less than 3.5. On the other hand, it is found that only 28.6% administrator did not agree
with this statement. Therefore, the statement is accepted. In a negative statement (item 12), a
significant amount of administrators (57.1%) did not agree that their graduates are not
competent to meet industrial requirement. The mean value, X for A = 2.81, is also low, which is
less than 3.5. Therefore, the statement is not accepted.
Figure 3.3 Challenges in TVET sector of Bangladesh
From Table 3.4 and Figure 3.3, we conclude that TVET sectors of Bangladesh are facing the
following challenges:
1.
Bangladesh has essential funding for skill training. Therefore, funding is not a major
problem in Bangladesh. (This statement is confirmed with the basis of qualitative data
and to get insight from document analysis).
2.
People have negative attitude towards enrolling in TVET sectors.
3.
Due to gender inequality, the majority of women have not been trained. Therefore,
gender inequality might be a challenge in TVET sectors. (This statement is accepted
based on the qualitative data, please see qualitative findings in page 68).
4.
There is a lack of long term plan (vision) for improving TVET sector.
5.
Vocational education is less popular (it has less social value).
6.
There is a shortage of specialized teachers in the vocational institutes. This findingmay
provide insight for the finding of number 5, Table 3.3. (see findings in success factors
where teachers perceived that the instructors in TVETsectors are competent toconduct
0,00 0,50 1,00 1,50 2,00 2,50 3,00 3,50 4,00 4,50 5,00
Bangladesh has necessary fund for TVET sectors
Have negative attitudes towards enrolling TVET sectors
Lesser women trained
Lack of long term plans for improving TVET sectors
Vocational education is less popular
Shortage of specialized teachers
High Female Skilled workers Unemployment
Language Barrier
It does not have adequate TVET institutions
Lack of competent instructors in TVET sectors
Youth opinions have not been taken
Graduates are not competent
Challenges in TVET sector of Bangladesh
X (Admin)
X (Teachers)
















