
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
182
5
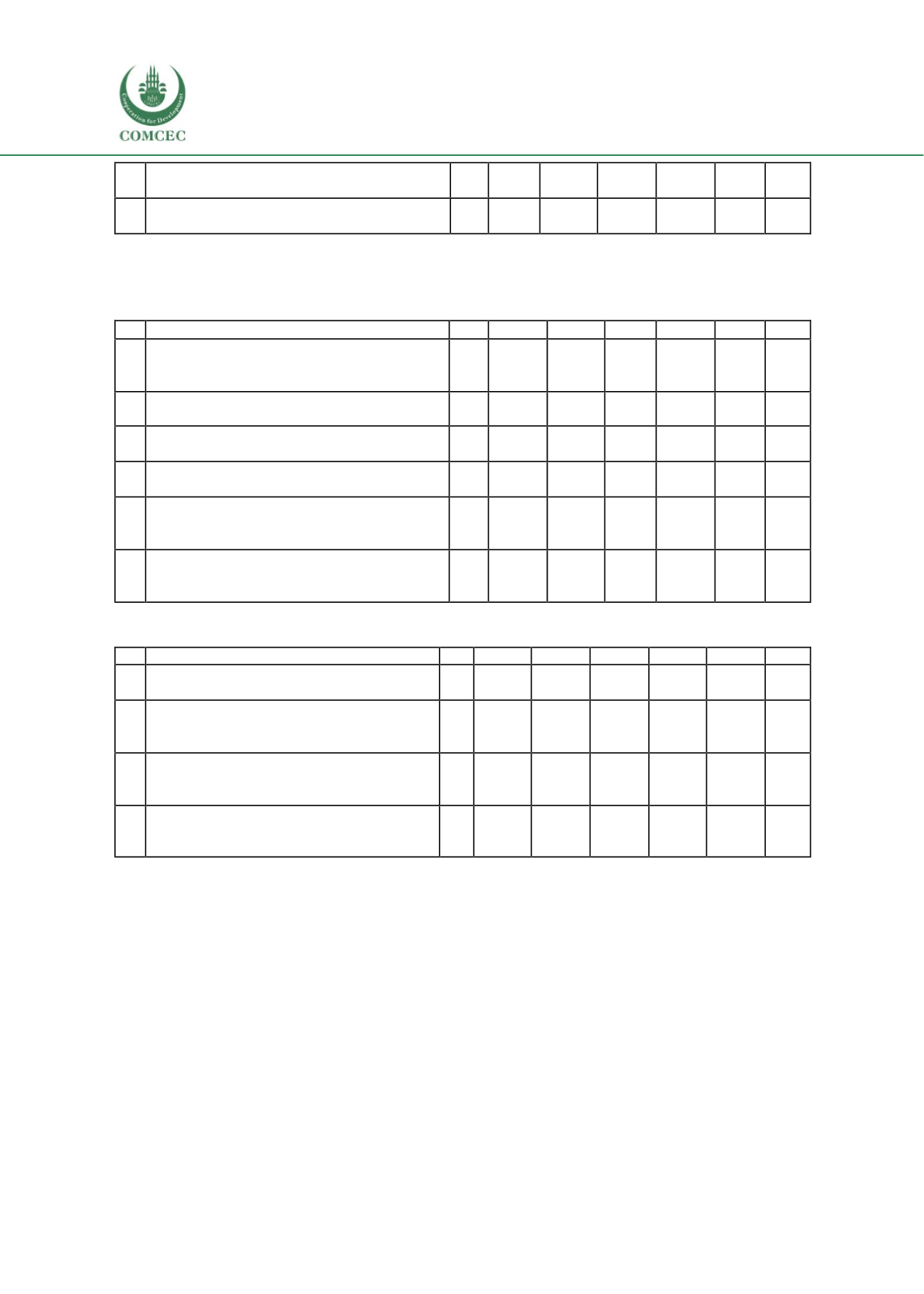
NGOs and other donor agencies provide
funds (aids) for skill training
21
16
76.2%
5
23.8%
3.76
6
NGOs and other donor agencies provide free
skills training for poor students
21
1
4.8%
13
61.9%
4
19%
3
14.3%
3.57
THEME 6: The challenges and the lessons learnt regarding vocational education (financial, socio -
cultural, lack of commitment etc.)
[Strongly Agree
(SA)
; Agree
(A)
; No option
(N)
; Disagree
(DA)
, Strongly Disagree
(SDA)
]
S
ITEMS
N
SA
A
N
DA
SDA
W
1
Poor people could not manage resources to
enrol for skill training (they need to work
hard for their living)
21
8
38.1%
10
47.6%
1
4.8%
2
9.5%
4.14
2
There is a lack of long termplans (vision) for
improving TVET sectors
21
6
28.6%
11
52.4%
2
9.5%
2
9.5%
4.00
3
Vocational education is less popular (it has
less social value)
21
9
42.9%
10
47.6%
1
4.8%
1
4.8%
4.24
4
There is a shortage of specialized teachers in
the vocational institutes
21
6
28.6%
13
61.9%
1
4.8%
1
4.8%
4.14
5
Government does not have any specific
policies for attracting poor people for
providing skill training
21
1
4.8%
4
19%
2
9.5%
10
47.6%
4
19%
2.43
6
Youth opinions have not been taken into
consideration while formulating policies for
the development of vocational education
21
2
9.5%
11
52.4%
2
9.5%
6
28.6%
3.43
THEME 7: The gap between vocational education and the needs of the labor market
S
ITEMS
N
SA
A
N
DA
SDA
w
1
Female skilled workers face higher level of
unemployment compared to male
21
3
14.3%
5
23.8%
3
14.3%
7
33.3%
3
14.3%
2.90
2
Outdated skill training that are not
compatible (matching) with the current
need of the labour market
21
4
19%
14
66.7%
2
9.5%
1
4.8%
4.00
3. There is no relationship between no of
TVET graduates and the skilled workers
needed in the industries
21
1
4.8%
8
38.1%
2
9.5%
7
33.3%
3
14.3%
2.86
4
Bangladesh cannot send many of their
skilled people in foreign countries due to
English or other language problem
21
15
71.4%
5
23.8%
1
4.8%
4.67
















