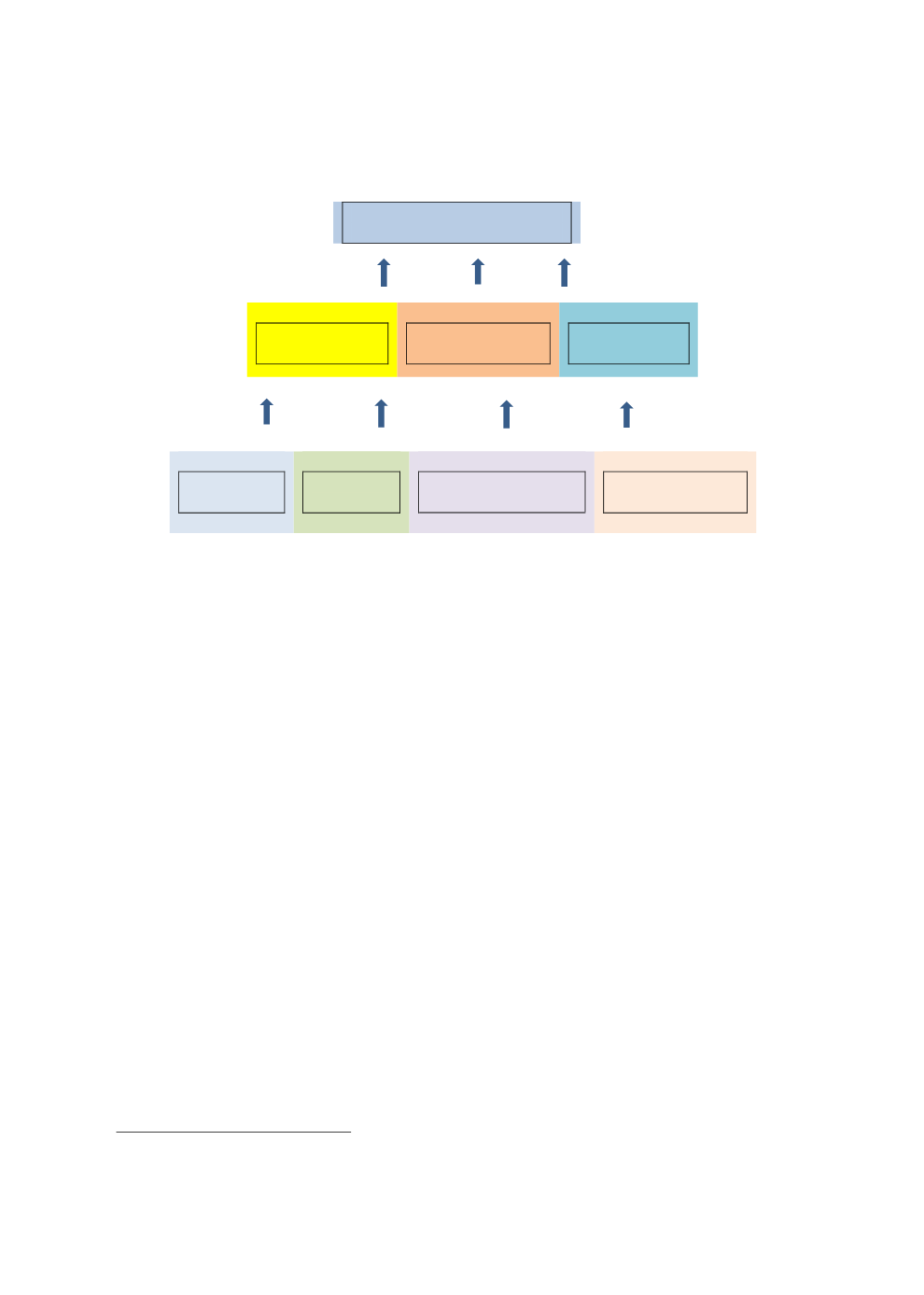
13
Figure 1.1: The Concept of Quality Education
Equitable Quality
Education
High
intake
High completion
rate
Full learning
experience
Teacher
quality
School
readiness
School management
& leadership
Physical facilities
in school
Source: Author, based on OECD-UNICEF (2016) and WDR 2018
Following the above framework, a quality education system is defined as one that achieves
inclusive education by ensuring intake, completion and learning as a function of teacher quality,
school readiness and household poverty, school management and leadership, physical
environment in school. Teacher quality refers to having formal qualifications as well as
motivation. School readiness factors include child health, early childhood development and
learning environment at home. It is assumed that these factors are determined by household
poverty and parental capability (particularlymaternal education). Child’s gender, age, disability,
language, location and citizenship status (migrants) can also affect school readiness and these
are recognized as important sources of inequality in learning opportunities
5
. Social customs can
dictate outside movement and interaction at a certain age different for boys and girls causing
gender gaps. Customs such as female genital mutilation and child marriage are other examples
of gender specific hurdles.
The OECD-UNICEF (2016) proposes an integrated “school as learning organisation” model
where “a school as learning organisation has the capacity to change and adapt routinely to new
environments and circumstances as its members, individually and together, learn their way to
realizing their vision”. The model focuses on:
1.
developing and sharing a vision centred on the learning of all students
2.
creating and supporting continuous learning opportunities for all staff
3.
promoting team learning and collaboration among all staff
4.
establishing a culture of inquiry, innovation and exploration
5.
embedding systems for collecting and exchanging knowledge and learning
6.
learning with and from the external environment and larger learning system
7.
modelling and growing learning leadership.
5
Balcazar, Narayan, and Tiwari (2015)