
Improving Road Safety
in the OIC Member States
143
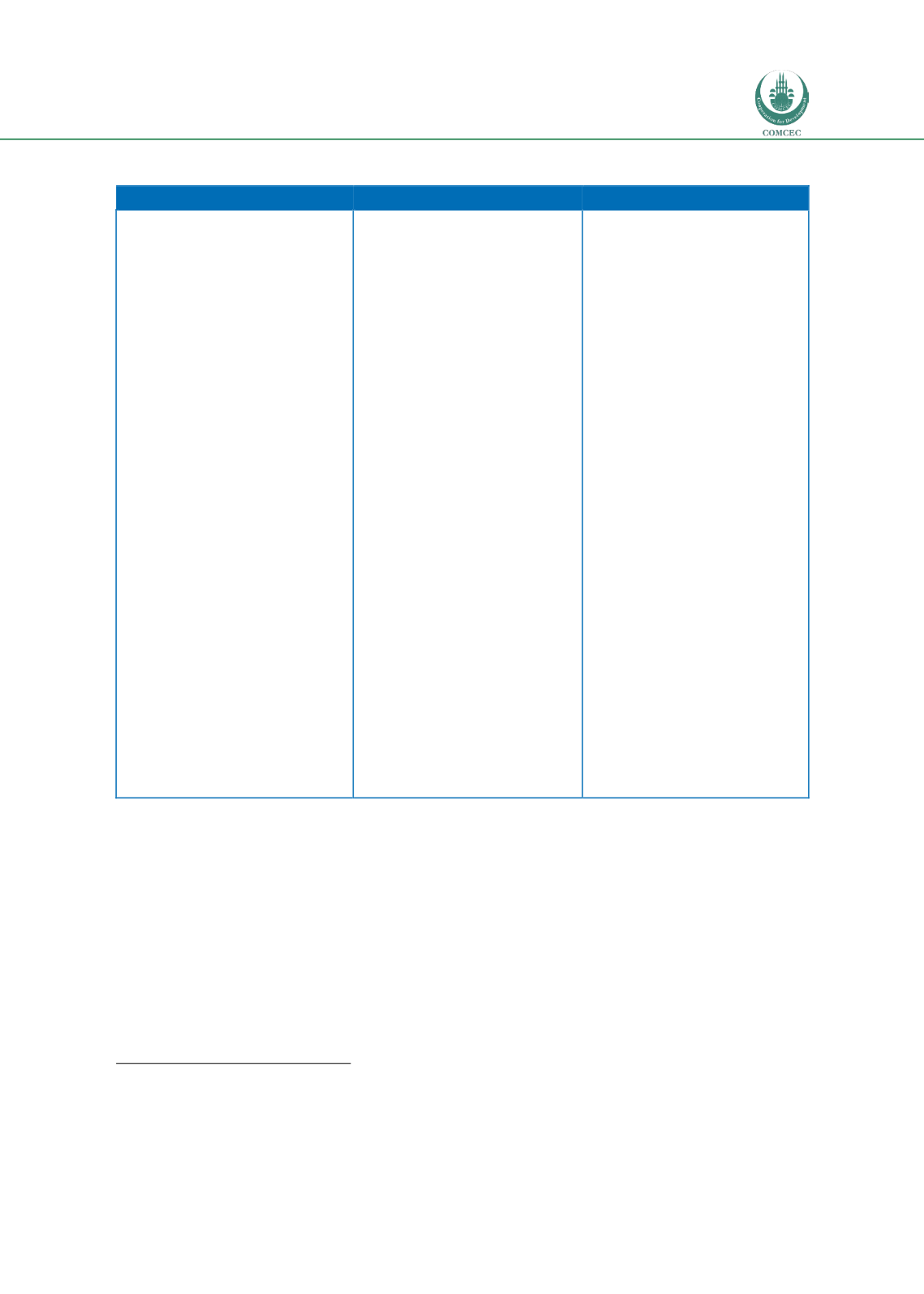
Table 28: OIC member countries and economic development
Low Income Countries
Medium Income Countries
High Income countries
Afghanistan
Bangladesh
Benin
Burkina Faso
Chad
Gambia
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Mali
Mozambique
Niger
Sierra Leone
Somalia
Tajikistan
Togo
Uganda
Albania
Algeria
Azerbaijan
Cameroon
Côte d’ Ivoire
Djibouti
Egypt
Gabon
Guyana
Indonesia
Iran Iraq
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kyrgyz Republic
Lebanon
Libya
Malaysia
Maldives
Mauritania
Morocco
Nigeria
Pakistan
Senegal
Sudan
Suriname
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Uzbekistan
Yemen
Bahrain
Kuwait
Oman
Qatar
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Source: Ecorys and SWOV
All of the OIC member countries are in the establishment or growth phase, based on both the
relationship between road safety performance and economic development and the road safety
characteristics per road safety development phase, as established in
Table 27713
. Some OIC
member countries, notably the LICs and the countries that score low on the Safe Systems
Approach, as established in Chapter 7, are in the establishment phase. For example, Gambia and
Togo have high mortality rates and score relatively low on the five road safety pillars and
development and use of road safety data
14
.
13
As argues above, some OIC member countries have advanced well towards a Safe Systems Approach, but
given the fact that these countries have not yet developed an integrated approach across all pillars
sufficiently, the countries are not yet in the maturity phase.
14
The five road safety pillars are rated in Chapter 7, mainly based on information provided in the annual WHO
global status of road safety reports.
















