
Improving Road Safety
in the OIC Member States
131
Tracing and enforcement
Tracing and enforcement are the responsibility of different police forces. The gendarmerie
(outside the built up area) and the police (inside the built up area) carry out regular road side
inspections. Both technical and driving proficiencies are checked. The police has no on line
access to the databases of the DTRSR. The police and gendarmerie have a copy of the vehicle
database and they can contact DTRSR among other things about updates, PTI, Motor vehicles tax
and insurance issues. Plans are being elaborated to establish an online connection. There is a
separate DTRSR inspectorate conducting road side inspection on driving and resting times
(tachograph) and the speed limiter.
According to 2008-2010 figures published by the Comité Permanent de la Securité Routière
(2011), there were about 4,000 monthly radar checks on speeding resulting in about 140,000
detected speed violations annually. On average a further 400,000 other traffic violations were
enforced and fines issued in 2008-2010 (Comité Permanent de la Securité Routière, 2011). Table
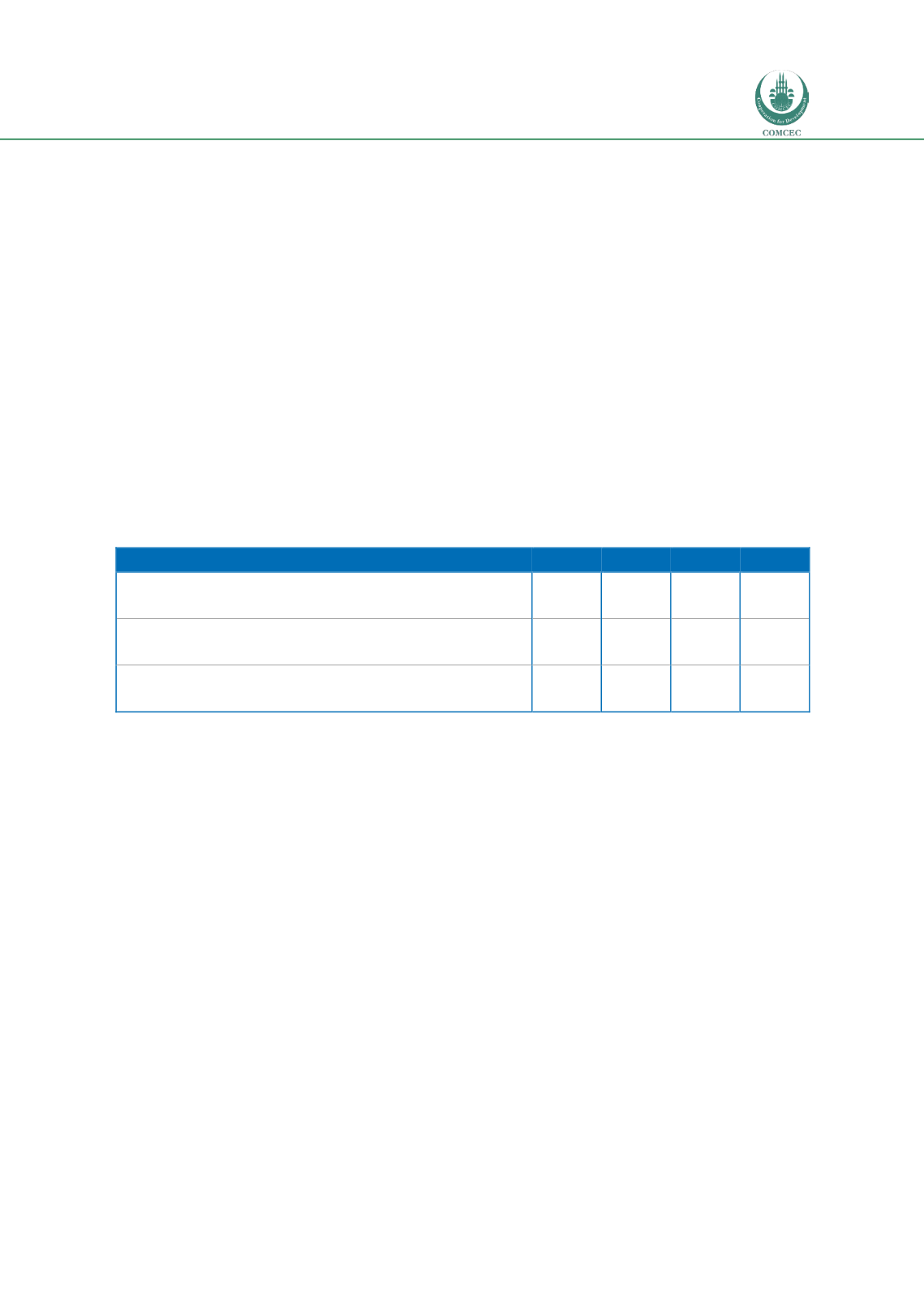
26 presents information on enforcement outcomes in period 2013-2016.
Table 26: Development of serious injury crashes
2013
2014
2015
2016 (*)
Direction Générale de la Sûreté Nationale:
traffic enforcement inside urban areas
505,718 643,053 663,165 503,739
Gendarmerie Royale:
traffic enforcement outside urban areas
527,153 670,084 749,661 554,631
Ministère de l'Equipement, du Transport et de la Logistique:
speed camera enforcement
202,450 465,757 401,046 1,010,930
Source: Official Road Safety Statistics Morocco (Ministre de l’Equipement et des Transports)
(*) from 01/2016 to 30/09/2016
Periodic technical Inspections
Annual Periodic Technical Inspections (PTI) for passenger cars is compulsory after five years.
For commercial vehicles and taxis the inspection is yearly. For buses the inspection is every six
months. The PTI is divided among five commercial organisations including DEKRA and SGS. The
inspections are conducted in PTI stations that only carry out the PTI. Maintenance and repair
are carried out by private workshops. The number of PTI inspection centres is about 250. 2,081
million vehicles have to be inspected because they’re older than 5 years or due to change of
ownership. Every station works with one or more “lines”. Pro line one can do pro day no more
than 20 inspections on light vehicles or 13 on heavy vehicles. If the vehicle passes the inspection,
a sticker is positioned on the inside of the front window. The information includes the next
inspection date.
The CNEH supervises the PTI stations in four different ways:
Random audits on the equipment, building, staff and vehicles that were checked;
Annual audits;
Statistical checks on the numbers of vehicles processed;
Independent audits by Veritas.
















