
Improving Road Safety
in the OIC Member States
1
Executive Summary
Rationale for focusing on road safety
Transportation is one of the six cooperation areas of COMCEC. The ambition is to help OIC
member countries to overcome transportation related problems in order to facilitate improved
movement of goods and passengers. As part of this endeavour, COMCEC has embraced the goals
of the United Nations (UN Resolution for the Decade of Action for Road Safety 2011-2020). The
“Decade of Action Resolution” calls for signatories to implement far-reaching road safety
programmes aimed at ultimately halving death and serious injuries in traffic related accidents
by 2020.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that more than 1.2 million people die on the
world’s roads annually. The majority of these deaths occur on the roads of middle and low
income countries and cost these countries approximately 3% of GDP annually. Traffic accidents
are preventable, yet they are still one of leading causes of mortality in todays’ society.
The WHO reveals that the annual number of fatalities worldwide seems to have stabilised.
However, this is primarily attributable to significant improvements in road safety management
in high income countries. Trends in middle and low income countries show a different picture
in which traffic mortality rates are disproportionately high. Low income countries have the
highest traffic mortality rate (24.1 deaths/100,000 inhabitants); almost three times that of high
income countries (9.2 deaths/100,000 inhabitants).
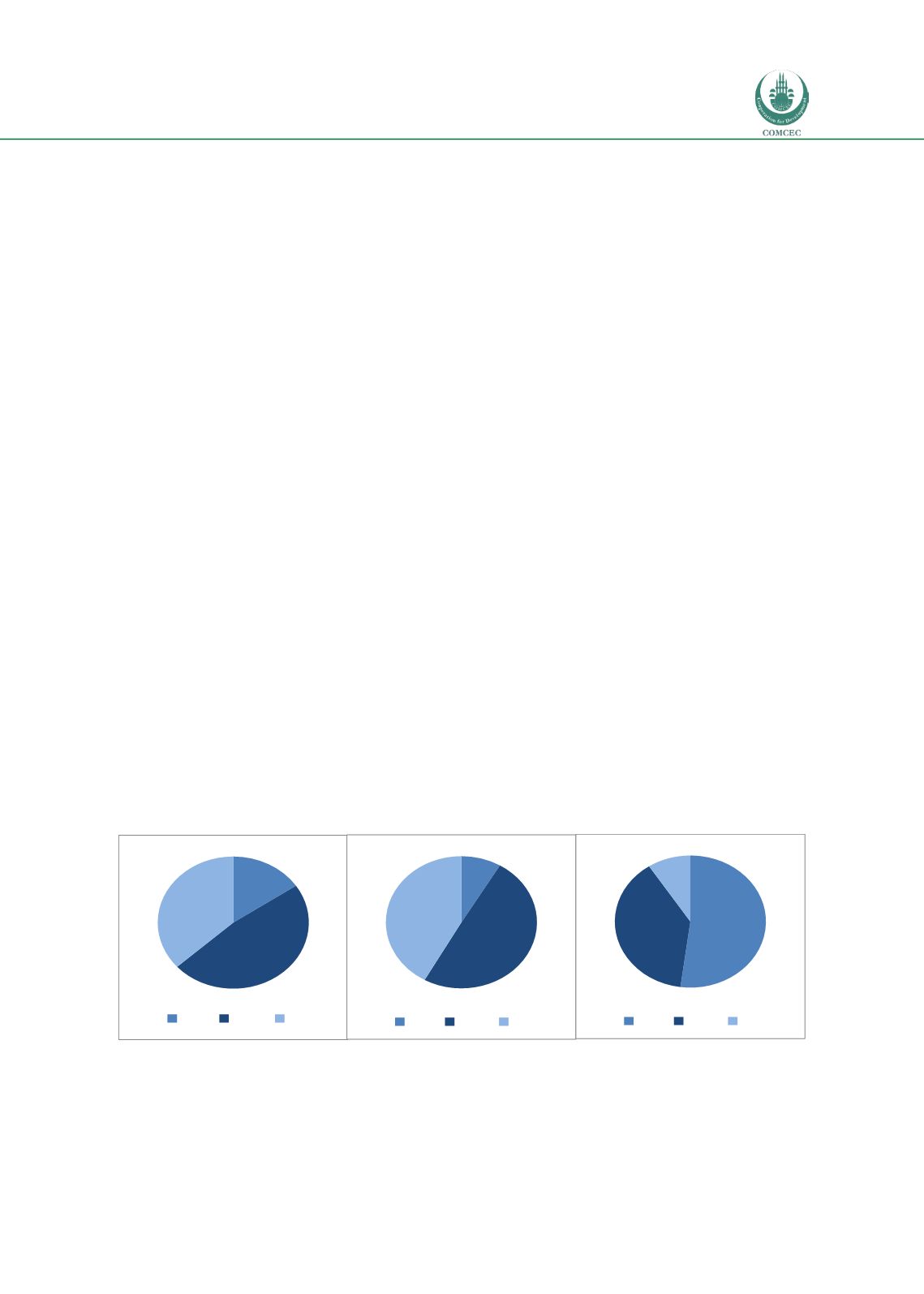
This is reflected in the figure below, which indicates that over 90% of road traffic deaths occur
in low and middle income countries, which have only 48% of the world’s registered vehicles.
Expected growth in car ownership and motorisation in low and middle income countries in the
coming decades will continue to put pressure on road safety in the low and middle income
countries.
Source: WHO, Decade of Action for road safety, 2011-2020
Population
Road traffic deaths
Registered vehicles
15,6
47,8
36,7
HIC MIC LIC
8,5
49,6
41,9
HIC MIC LIC
52,1
38,7
9,2
HIC MIC LIC
















