Improving Transport Project Appraisals
In the Islamic Countries
76
4
Results case studies: Afghanistan
This chapter presents the results of the case study Afghanistan, following the structure of the
conceptual framework, as developed in Chapter 2.
4.1
Introduction
The process which Afghanistan has gone through over the course of two decades have had
significant consequences on the country’s physical transport infrastructure and on its human
and financial resources. As a result, managing the national transport sector, including planning
and appraising of transport projects, has been challenging.
In order to address the above-mentioned challenges, Afghanistan has embarked on a number of
international collaborations to restore the country’s industry. For example, the
ADB
has been
working closely with Afghanistan’s public institutions in developing a
strategy-course
to be
implemented through a number of significant investments and development measures. To this
end, the ADB assisted in developing the Afghanistan
Transport Sector Master Plan Update
(ATSMPU) 2017-2036
. The proposed strategy presents a
comprehensive list of infrastructure
projects
to be developed, and
capacity-expanding measures
to be implemented across all
prevailing transport sectors. The ATSMPU concludes that in an unconstrained resource
scenario, the investment requirements over the following 20 years amounts to a total of $25.9
billion.
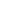
Table 4.1illustrates how this total sum of investments is to be decomposed across
individual transport sectors.
Table 4.1: Total investment requirements per transport sector (2017-2036)
Source: Afghanistan Transport Sector Master Plan Update (2017-2036)
The following sections will expand on those aspects of the ATSMPU, as well as other supporting
documents, which provide valuable insights to the current appraisal practices regarding
transport infrastructure projects in Afghanistan.
4.2
Legal basis
The current legal framework for the development of infrastructure projects is limited to the
planning and budgeting phases. According to this framework, the planning of projects follows a
bottom-up approach, in which local councils identify necessary projects according to their
needs. These proposals are then submitted to the Central Government for further screening and
prioritisation. The aid cooperation department of
Ministry of Economy
(MOE) is then responsible
Sector
Amount ($ million)
Share (%)
Railways
11,176
43.1
Roads
13,000
50.2
Urban transport
853
3.3
Airports
568
2.2
Trade facilitation
300
1.2
Total
25,897
100.0