Improving Transport Project Appraisals
In the Islamic Countries
49
intended as an illustration. In the Netherlands, a time horizon of 100 years is commonly used.
The present value for each item in the CBA is calculates using the discount rate that is prescribed
by a discount rate working group. For transport infrastructure projects, usually a discount rate
of 4.5% is used. The result of the CBA can be presented as a NPV, IRR and benefit-cost ratio
(BCR).
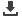
Table 2.1: Example CBA
Example CBA
Present Value
2019
2020
2021
….
2118
Costs
Investments costs
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
Maintenance costs
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
Noise pollution
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
Safety costs
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
…
Total costs
€0,0
Benefits
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
Travel time savings
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
Employment
€0,0
0
0
0
0
0
…
0
0
0
0
0
…
0
0
0
0
0
Total benefits
€0,0
Results CBA
NPV
XX
BCR
XX
IRR
XX
Source: Ecorys
The market price is used for the estimation of costs and benefits. Regarding improved reliability,
it is recommended to estimate it by assuming an amount of 25 percent of the value of travel time
gains (or losses).
2.1.5 Demand analysis
The consequences of the project for travel expenses, travel time and frequency play a role in
making transport forecasts. The benefits of an infrastructure project depend very much on the
effects of the project on transport flows. These effects are determined by individual behaviour
of users and operators. Therefore, it is recommended to use a forecasting model to predict the
effects on transport flows. The transport prognosis is not only the basis for calculating direct
effects; the indirect effects of the project could be strongly related to the direct transport effects.
Different traffic and transport models are used in the Netherlands. Provinces and municipalities
often use regional or local models to make detailed traffic forecasts. The Ministry of
Infrastructure andWater Management uses two strategic models for the main road network and