Planning of National Transport Infrastructure
In the Islamic Countries
117
Planning processes are highly centralized
and follow a simple structure as all funding is coming
from government and is state-based. The Ministry of Finance can either approve or reject a
project, once this has been assessed according to its impact. Recently Qatar added traffic impact
as a new and additional criterion in its projects assessment.
The centralized and strong position of the state limits the role of private companies, whose
impact is of minor importance. However this is about to change as the Qatar government is
transiting to a PPP model where finance and risk borne by the state are reduced to 70%, from
the original 100%, opening doors to private parties. Aim of this transition is to accelerate
developments and to reach the national objectives.
International transport infrastructure related agreements do have a large influence on Qatar’s
NTI plans. These agreements have an impact on the supplies, the logistics and the regional
transportation market and define the border transportation facilities.
3.5.2.
Institutional and Organizational Factors
Assessing the institutional response to transport planning in Qatar, it is necessary to consider
the fundamental role of the state both in planning and in funding. Despite the progressive
opening to PPP, investments and initiatives in the transport sector are still mainly coming from
the state.
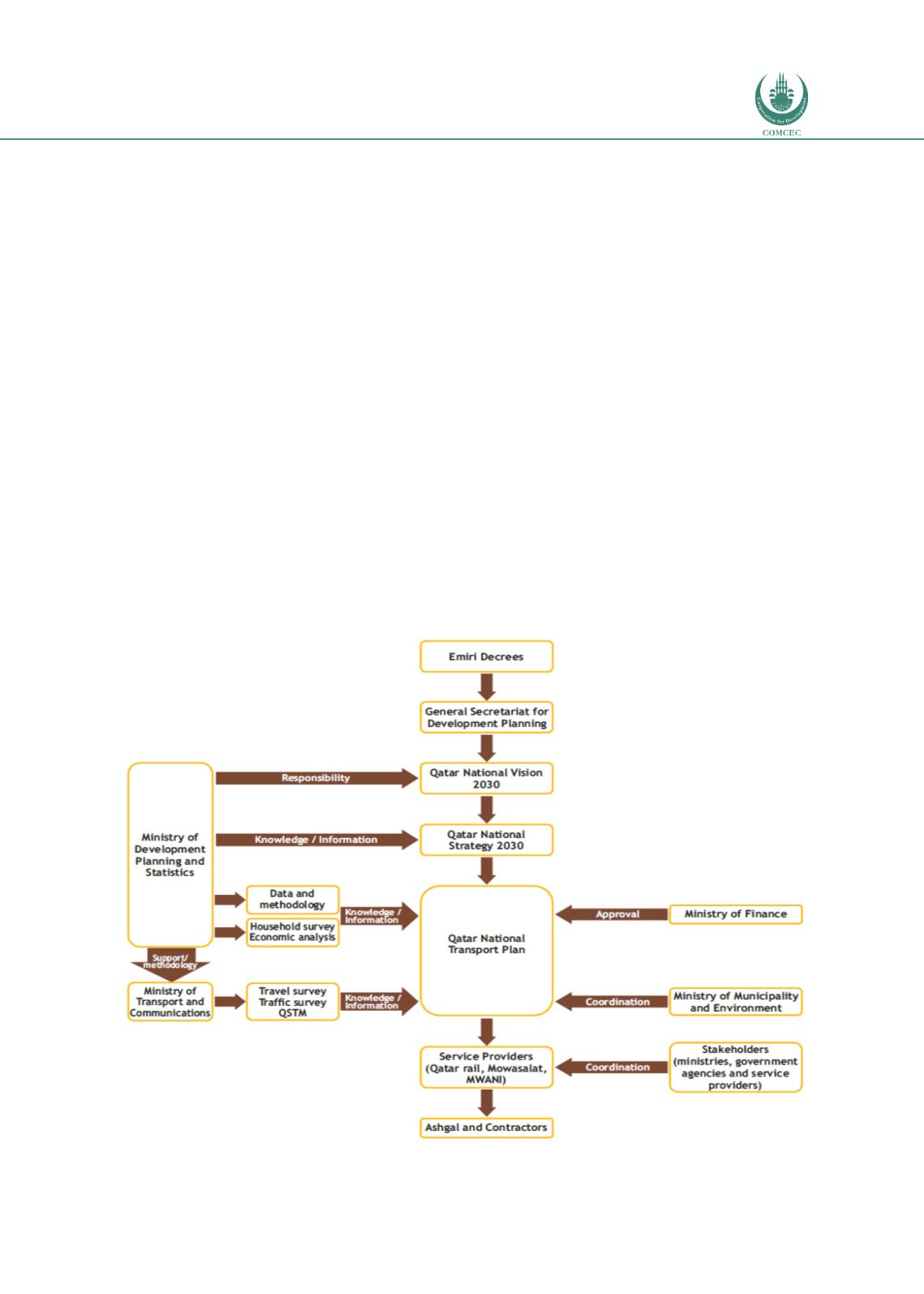
The transport infrastructure planning process in Qatar is summarized in the following diagram.
Figure 32: Development Process of Qatar National Transport Plan