Governance of Transport Corridors in OIC Member States:
Challenges, Cases and Policy Lessons
83
5.3.7
Promotion and stakeholder consultation
ALCO is regularly organizing stakeholder consultations on issues related to operations of the Abidjan-
Lagos Corridor, in particular related to the combat of STIs and HIV infections, trade and transport
facilitation including harmonization of rules and regulations concerning international transport, and
road safety. The 2017 MoU on the development of the Abidjan-Lagos Highway signed by the
Participating Member Countries of the Abidjan-Lagos Corridor includes: “The Communications and
Public Relations’ tools including a video documentary, a corridor logo, brochures and flyers, were also
endorsed as an instrument of creating awareness and the generation support of the ECOWAS
authorities and community citizens for a successful implementation of the Project”
35
.
5.3.8
Capacity building: technical assistance and studies
The major part of capacity development, technical assistance and studies has been provided by
international development cooperation agencies (World Bank, European Commission, African
Development Bank, bilateral organisations, etc.), and sometimes through regional organisations as
ECOWAS and the West Africa Economic and Monetary Union (WAEMU)/UEMOA).
5.3.9
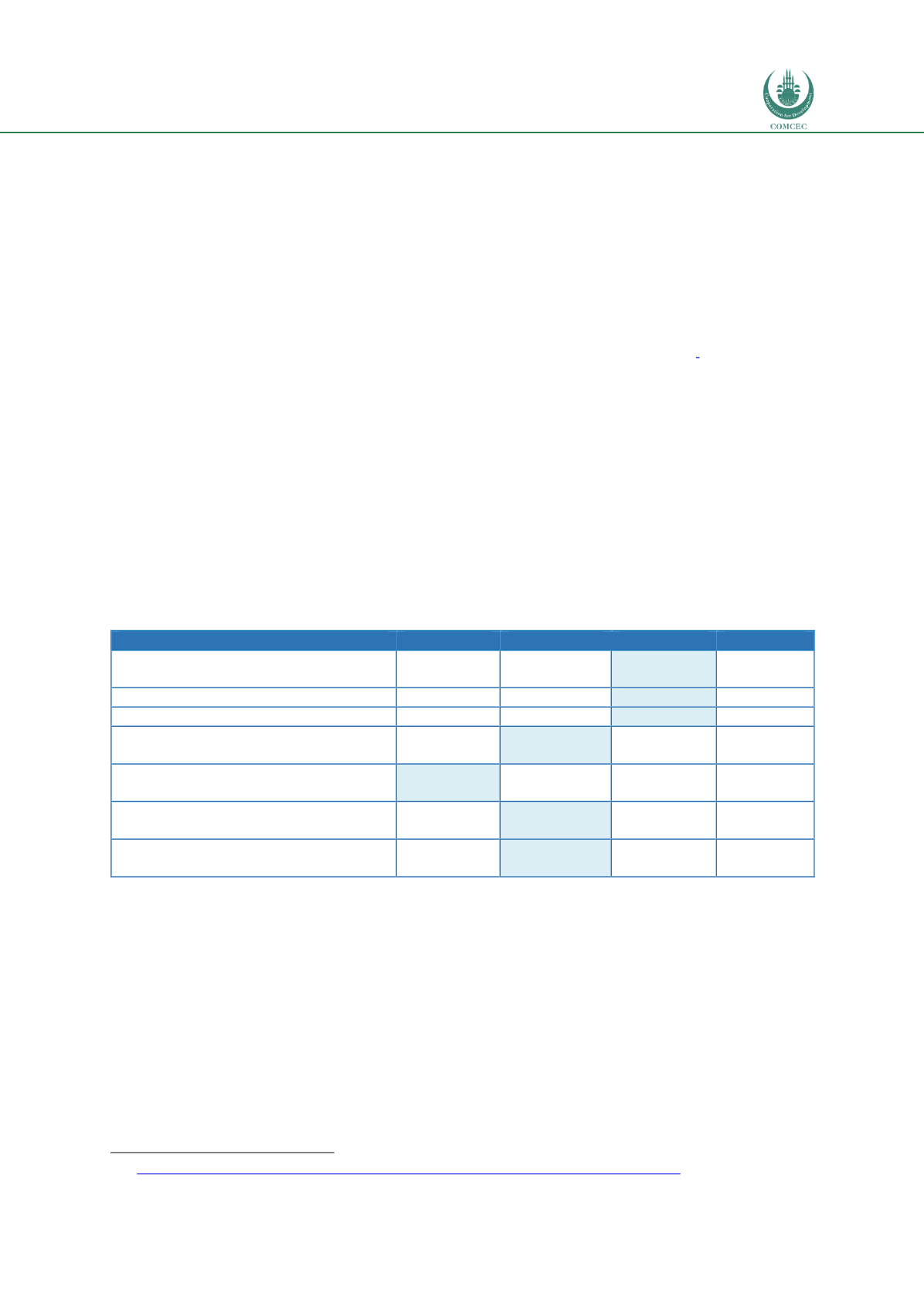
Assessment of transport governance level
The seven corridor governance domains of the ALC, as presented in this section, are ranked against
the four defined corridor governance levels (information exchange; coordination; cooperation;
integration), as introduced i
n Table 2.9.The ALC governance levels are presented below.
Table 5.3 ALC governance levels
Governance domains
Information Coordination Cooperation Integration
Corridor objectives and political
support
Legal framework
Institutional framework
Infrastructure: financing, planning and
programming
Corridor performance monitoring and
dissemination
Corridor promotion and stakeholder
consultation
Capacity building: technical assistance
and studies
Source: consortium.
5.3.10
Conclusions
ALC and ACLO were established in 2002 on a project basis funded by the World Bank. Its main goal
was to prevent the spread of HIV/AIDS in the field of transport. Later, other objectives had been
defined such as cross border trade facilitation and reducing waiting times at border crossings as well
as improving road safety along the corridor. Increasingly, ACLO facilitated the implementation of
transport measurements, often within the framework of ECOWAS, however the weak legal and
institutional basis and the lack of resources made its impact limited. Some major developments have
been made in de last years when the five Participating Member States (PMSs) started to work together
on a large scale infrastructure project, the Abidjan-Lagos Highway financed through the African
35
http://www.ecowas.int/experts-finalise-the-draft-design-legal-framework-of-abidjan-lagos-corridor/.