Governance of Transport Corridors in OIC Member States:
Challenges, Cases and Policy Lessons
35
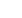
Table 3.2 Current legal framework for the development of TEN-T
Regulatory
Area
Legislation
TEN-T
development
Regulation (EU) No 1315/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 11
December 2013 on Union guidelines for the development of the trans-European
transport network and repealing Decision No 661/2010/EU (OJ EU L 348,
20.12.2013, p. 1).
Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/758 of 4 February 2016 amending
Regulation (EU) No 1315/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council as
regards adapting Annex III thereto (OJ EU L 126, 14.5.2016, p. 3).
Harmonization of national regulations, standards and procedures
The EU actively seeks to improve its transport system by harmonizing regulations between the
members. By now, there are over 100 regulations for rail, road, air and waterborne transport. As an
example, all the regulations for road transport are shown i
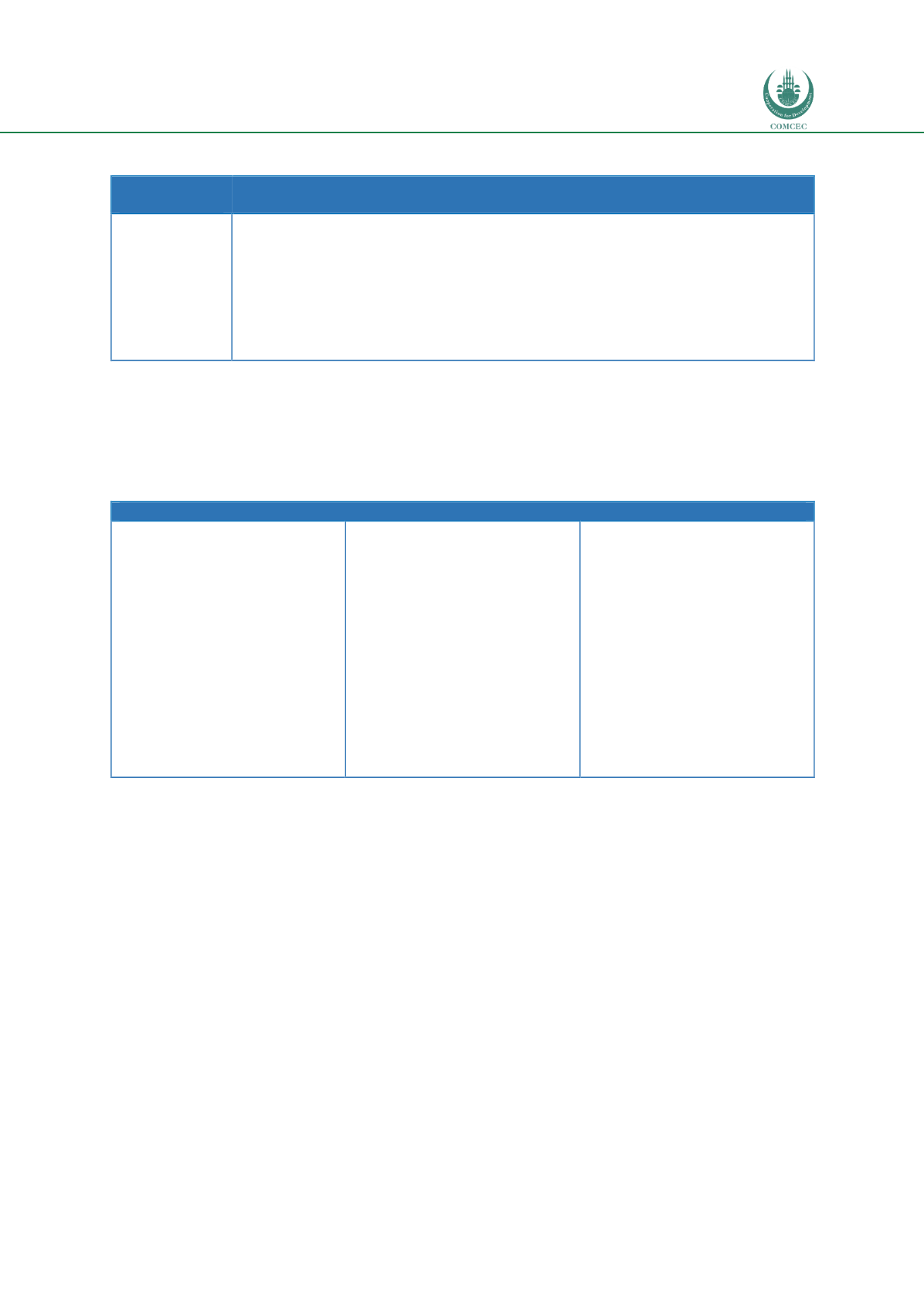
n Table 3.3.Table 3.3 European regulations on Road transport
Regulations on road transport
Road charging
infrastructure;
Admission to the occupation
of road operator;
Social provisions – driving
time and rest periods;
Tachograph;
Enforcement of social
legislation;
Form of attestation of
activities;
Working time;
Roadworthiness;
Mirrors.
Registration documents;
Training of drivers;
Driving license;
Cross-border exchange of
information;
Inland transport of
dangerous goods;
Checks on transport of
dangerous goods;
Tunnels;
Transportable pressure
equipment.
Roads infrastructure safety
management;
Dimension and weight of
vehicles;
Passenger rights;
Clean vehicles;
ITS;
Road toll systems;
Type approval;
Roadside Inspection;
Speed limitation devices;
Safety belts.
Source: consortium.
3.1.3
Institutional framework
Organization and characteristics
As the EU deals with many more policy terrains besides transport, the governance structure is
complex. On an EU-wide level, the decision-making body consists of:
European Parliament: EU’s directly elected law-making body;
European Council: in which government ministries meet and discuss policies. The European
Council is equivalent to the ministerial meetings of other corridors.
Policy making starts with the European Commission, which implements policy based on decisions
made by European Parliament and European Council. Within the European Commission, DG MOVE
(Directorate-General for Mobility and Transport) is responsible for transport within the EU, and:
Develops and carries out the Commission’s policies on transport;
Manages the Connecting Europe Facility Funding programme, a funding instrument available for
infrastructure investments;