Improving Transnational Transport Corridors
In the OIC Member Countries: Concepts and Cases
56
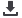
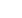
Figure 21: Intermodal transport - railway piggy back
Source: Canadian National Railways.
Investment Phasing and Costs
The master plan will be implemented over three five-year intervals - short term (2012-2017),
medium term (2017-2022) and long term (2022-2027). This is in line with the SADC Vision
2027, a 15-year implementation horizon for forecasting infrastructure requirements in the
region. It is also in line with the African Union's
Program for Infrastructure
Development in Africa (PIDA)
and will constitute a key input into the Inter-Regional
Infrastructure Master Plan and proposed tripartite Free Trade Area of SADC, the COMESA,
and
the EAC
.
The total investment requirements are $ 860 Billion for the RDIMP as shown i
n Table 5.Table 5: SADC RDIMP Investment Needs
Sector
Program Description
Initial Investment Cost
(USD) Billion
Energy
Energy generation and grid connections
236
Transport
Construction and Maintenance
100
ICT
Complete broadband connectivity
383
Meteorology
Improved equipment, manpower, expertise
125
Water
Investment Projects and Studies
15
Tourism (TFCAs) TFCA Facilities Investment Plans
1
Total
860
Source: SADC Transport Master Plan (2012).
The total investment requirement for the transport sector was estimated to be $860 Billion.
SADC expects that over 70% of the funding to come from the private sector. When the