Sustainable Destination Management
Strategies in the OIC Member Countries
34
consumption of local products, the support of local businesses, decent employment, and social
responsibility.
104
Still, ensuring local community well-being is a key and long-term challenge for
sustainable tourism development.
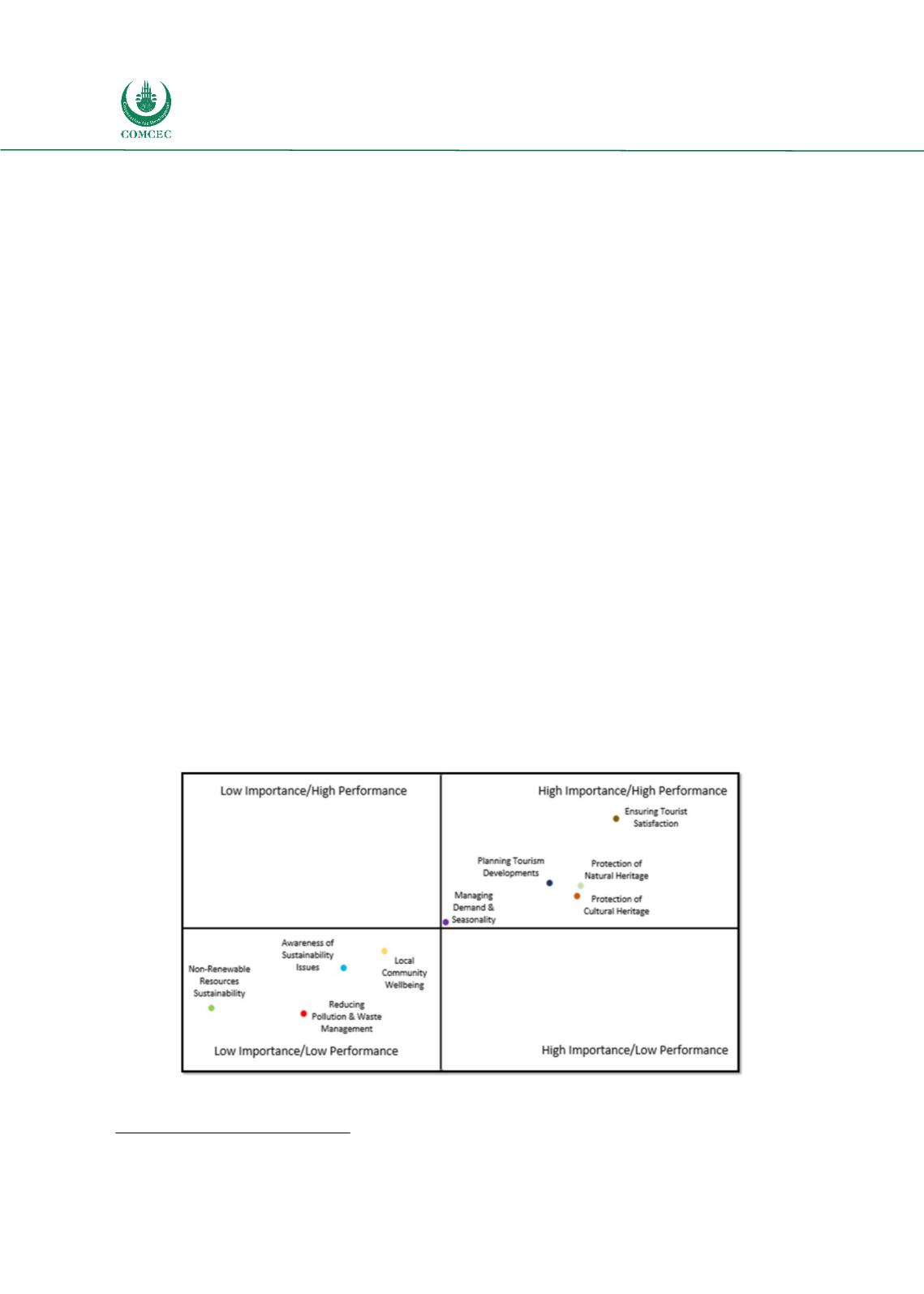
Survey Insights
The survey findings suggest that respondents believe that their respective destinations are to a
large extent addressing the strategy areas that should to be prioritized. The following matrix
shows that the strategies that were rated higher in terms of priority by the respondents were to
a great extent addressed efficiently, while the strategy areas the respondents considered to have
lower priority also had lower levels of performance. The strategy area the respondents rated the
highest in terms of both importance and performance was ensuring tourist satisfaction.
Protection of natural and cultural heritage, and planning tourism developments were rated
higher in terms of priority than managing demand and seasonality, which also had the lowest
performance rating in the high-performance strategies. With respect to the strategy areas that
were rated by respondents lower in terms of importance, most of the strategies in this category
were those related to the environmental and social dimensions of sustainable tourism, which
can be due to the fact that survey respondents were mostly industry professionals who are more
worried about the economic dimension of sustainable tourism. The area that received the higher
priority as well as higher performance rating was that of local community wellbeing. It is
important to note that while respondents may have assigned lower priority to strategies such as
local community wellbeing, non-renewable resources sustainability and reduction of pollution
and waste management, these strategy areas are being considered as priorities in most
destinations’ current tourism strategies. From this perspective, the fact that these areas were
lower in performance levels indicates lower focus on these areas. This sheds a light on the
importance of creating awareness of the importance of the environmental and social dimensions
of tourism sustainability.
Figure 5: Sustainable Tourism Strategies Importance Performance Matrix
Source: DinarStandard
104
Please refer to Denmark’s case study for further information and sources.