
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
10
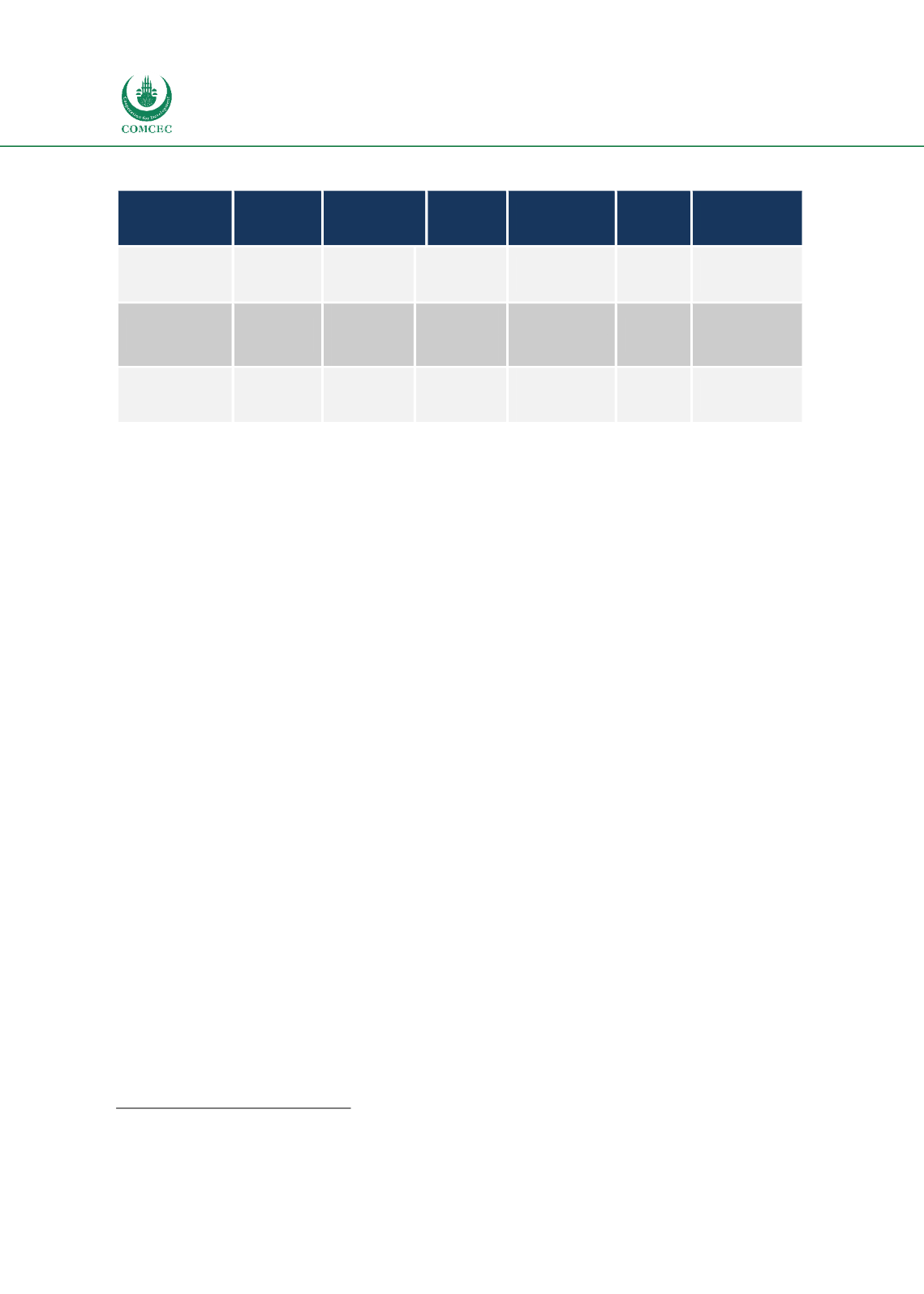
Table 2: Evaluation of the Information on the Strategic, Tactical and Operational levels
Management
Level
Time
Period
Frequency
Source
Certainty
Area
Scope
Strategic
Long-
term
Low
Mostly
External
Less Certain
Broad
Summarized
Tactical
Midterm
Medium
Ad hock
Internal/
External
Medium
Certainty
Specific
Detailed
Operational
Short-
term
High
Mostly
Internal
More
Certain
Specific
Detailed
Source: Authors compilation based on Bocij P., Greasley A.: Business Information Systems: Technology, Development and
Management for the e-Business
The WCO Risk Management Compendium (Volume 2) describes the following sources of data
that are internal to a CA: seizure reports; strategic, tactical, operational reports of other Customs
administrations; intelligence data; information exchange with other Customs Administrations;
risk signals from Customs officers and other law enforcement personnel; cooperation or
interviews with other knowledgeable people from the import and transportation trade, e.g.
Customs brokers, cargo agents, warehouse personnel, etc., transport documents such as
manifests, airway bills, etc., available national Customs (or other law enforcement agencies)
databases, signals and alerts.
It’s now common to divide sources of information two different types: external and internal
information. The information used in CRM can also be categorized as primary and secondary
sources of information. The primary source of information includes interviews, reports and
other first-hand information
5
. Secondary sources of information are publicly available
information, whether they are coming from within the organization or from the outside that
provides:
Internal search for multiple types of information such as databases, text documents,
reports, visual objects such as maps and graphs, e-mail and intranet discussions.
An external search of web-based sources such as web pages, messaging services, and
databases.
Comprehensive, adaptable word-based searches, phrases, concepts, dates, and other
search capabilities.
Web indexing using a "spider" application based on predefined queries by the user.
Sources of risk management at border crossing points for goods clearance can be divided as
follows:
Intelligence products created at the local and regional customs intelligence offices and
strategic intelligence products created at the central customs headquarters;
Information sharing with other government and law enforcement agencies;
Information and feedback based on customs controls, in the form of seizure reports;
5
Fuld L. M.: “Intelligence Software Report 2008‐2009”, Fuld & Company
(http://quoniam.info/competitive-intelligence/PDF/ebooks/fuld_CI_2008_review.pdf)
















