Improving Customs Transit Systems
In the Islamic Countries
30
Sourcing goods directly at the point of importation – a seaport – is clearly an advantage. On
average, thanks to lower freight costs, retail gasoline price is usually few cents lower in seaports
than in the inland areas of the same country. However, the retail prices are affected by many
additional cost factors in addition to the transport alone, primarily the excise taxes, which in
Europe account for 75-95% of the retail price. As a result, due to lower tax structure, landlocked
North Macedonia has lower gasoline prices than Greece, even as it mainly imports its oil and oil
derivatives via the Greek port of Thessaloniki. This anomaly may occur in other sectors, such as
textile products in landlocked Uganda, which are cheaper than in neighboring Kenya. Overall,
the natural advantage of having a seaport will always remain a factor; however, efficient trade
facilitation measures and free trade agreements, in conjunction with more competitive
(cheaper) transport, will minimize this difference.
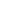
Table 2: Average Trading across Border Score and LPI score
Maritime Landlocked
EU
EU
candidates
All
Trading across Borders Score
69.61
75.40
97.39
93.16
70.86
Time to import: Border compliance
(hours)
5.67
58.07
1.71
11.20
17.04
Cost to import: Border compliance
(USD)
434.78
251.05
29.21
126.20
394.92
LPI Score
2.93
2.67
3.54
2.82
2.87
Source: Author own compilation
If we compare this data with the EU countries that use the common transit system, there is a
large difference. Average trade across border score for all countries in the database is 70,86,
while the average in EU countries is 93,16, and even some EU candidate countries have a higher
score than the global average. The same case is regarding time and cost to import for border
compliance and LPI score. Therefore, an efficient CTR is an important part of the individual
performance of the countries.
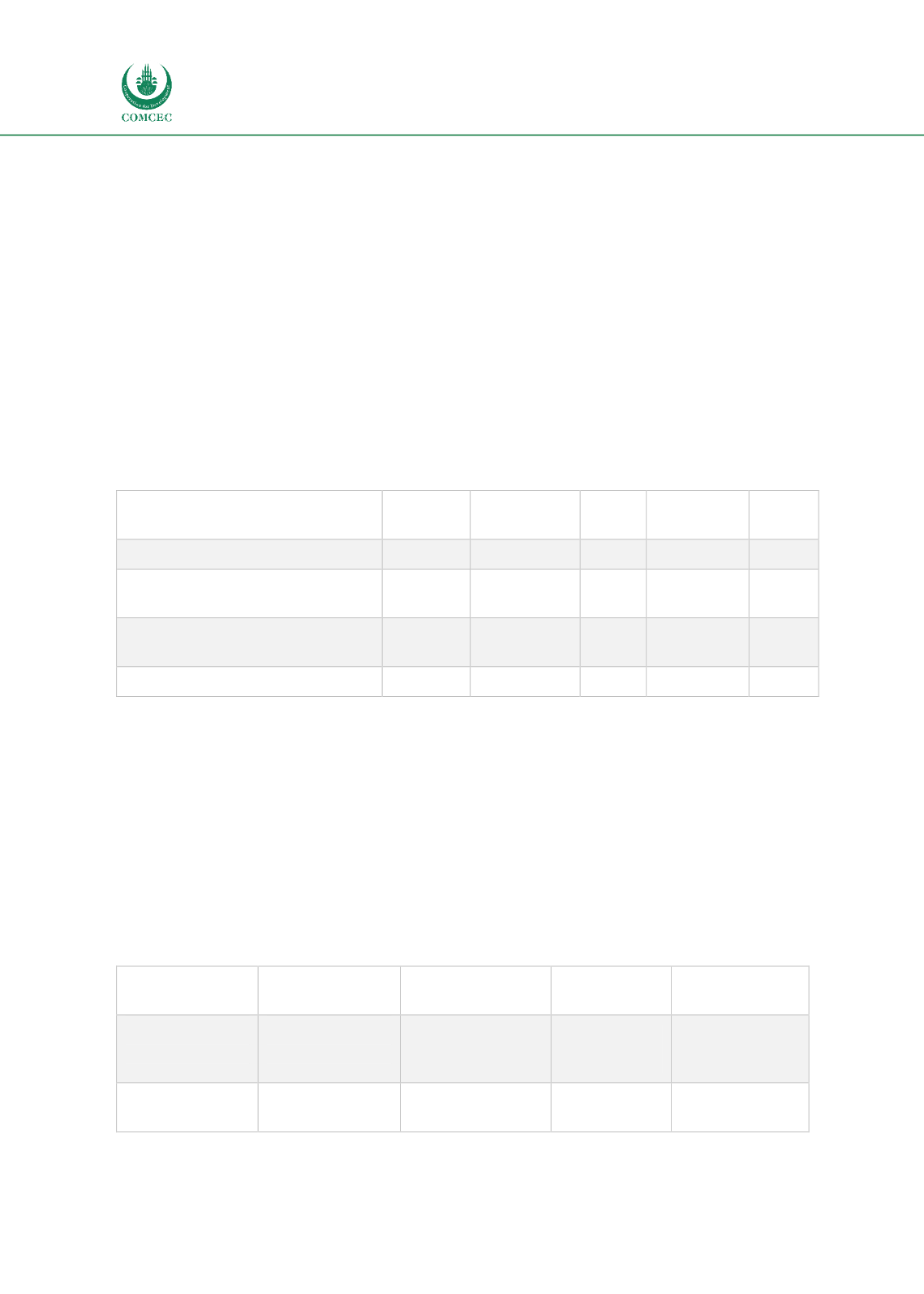
Table 3: Benefits of efficient CTR for Customs, Business Sector, Transporters, National
Economy and Regional Economy
Customs
Business Sector
Transporter
National
Economy
The region as a
Whole
Reduced costs for
transit
procedures
Reduced costs to
import
and
export of goods
Reduced
service
costs
Reduced trade
costs
Reduced
trade
costs
More advanced
Risk Management
Higher
trade
volume
More
transport
services demand
Increased
trade volume
Increased trade
volume