FACILITATING INTRA-OIC TRADE:
Improving the Efficiency of the Customs Procedures in the OIC Member States
40
to Article 6.5, the Customs shall adopt a compliance measurement strategy to support
risk management.
The ICC Customs Guideline 16 also shares the same view with the RKC and states that
modern customs “Uses selectivity, based on automated compliance measurement and
risk-assessment and profiling systems, to target suspect consignments and so minimize
the incidence of physical examinations”
The Article 4.3 of WTO Trade Facilitation Agreement gives some idea on the
selectivity. The Article states that risk management shall be based on risk management
on assessment of risk through appropriate selectivity criteria which may include, inter
alia, HS code, nature and description of the goods, country of origin, country from
which the goods were shipped, value of the goods, compliance record of traders, and
type of means of transport.
The WCO developed Risk Management Compendium which provides guidance for the
countries in implementing the risk management. According to this Compendium, risk-
based compliance management approach requires the creation of a robust organizational
risk management framework, which provides the foundation and organizational
arrangements allowing individual risks to be identified, assessed and managed across
the Organization and empowers officers at all levels to make risk-based decisions in a
structured and systematic manner. European Commission (2007) also suggests that, for
effective implementation of the risk management, the process should cover the
following: context, risk analysis, treatment and monitoring (See Box 3 below).
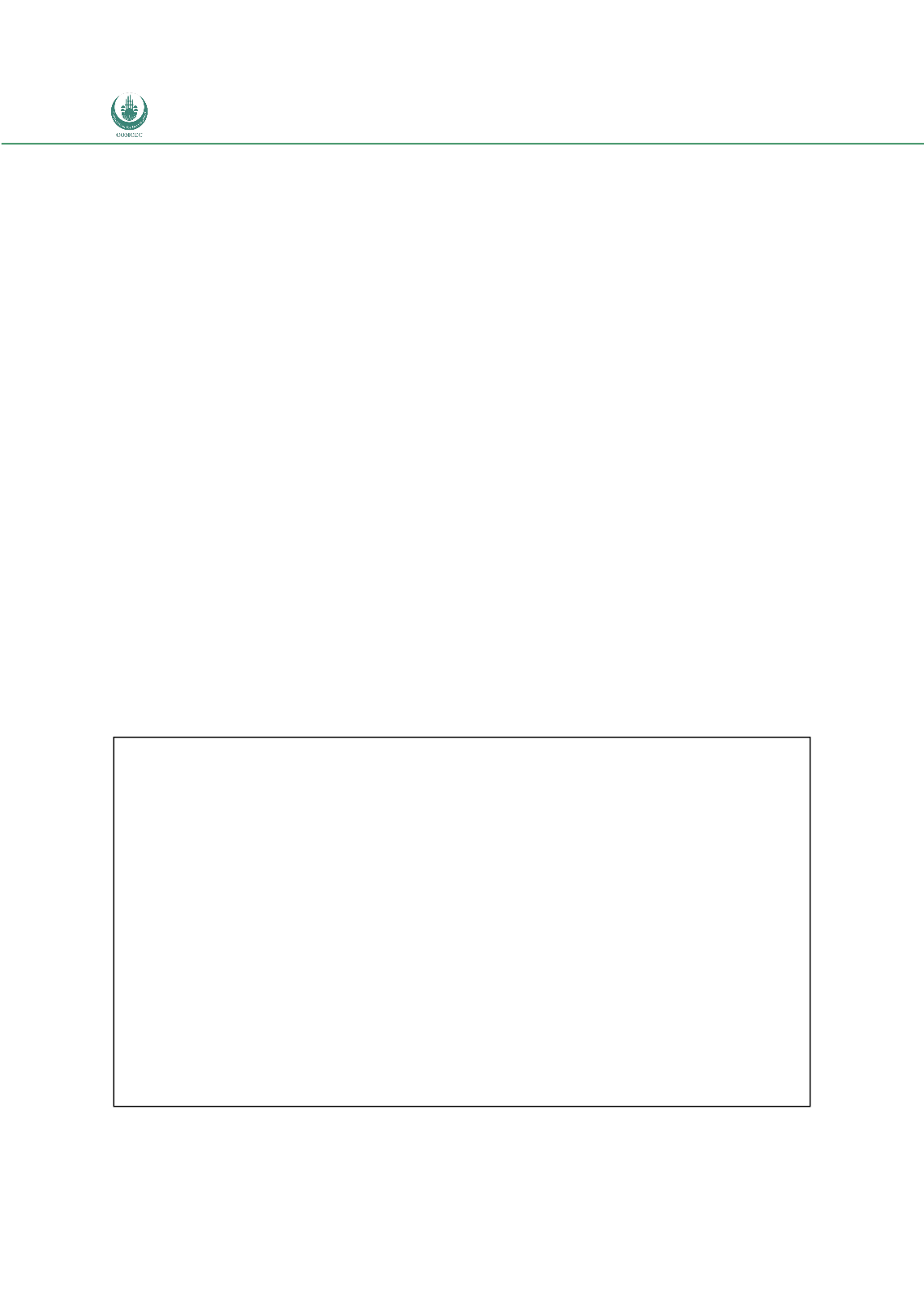
Box 3: Risk Management Process
The risk management process comprises the following:
– Context is the environment in which the risk management process is performed and can be
influenced by various factors such as resources, and political, legal and social circumstances.
– Risk analysis examines and evaluates all available information for operational purposes. Information
can be gathered from various sources, such as arrest and seizure records, locally and internationally,
other law enforcement agencies, traders and other governmental authorities.
– Treatment of risks is the action to be taken (documentary or physical). Once risks have
been identified, analysed and assessed, action must be taken to prevent the risks from occurring or to
minimise the consequences if they do.
– Monitoring and review looks at the performance, effectiveness and efficiency of the risk-
management system and changes that might affect it.
Source: European Commission (2007) “Customs Blueprints: Pathways to modern customs”