Special Economic Zones in the OIC Region:
Learning from Experience
61
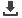
Figure 11 – Average Monthly Downtime due to Power Outages – SSA African SEZs
Source: Farole 2011
Infrastructure provision is an acute challenge with many zones constrained by the quality and
provision of infrastructure. Power, gas, roads, ports and telecom infrastructure are particular
challenges and there has been a recent trend with regards to Public Private Partnerships (PPP)
to solve these constraints. Given the typical size of investments required to service these zones
however, there is a strong requirement for solid commitment for Government for these projects
alongside active participation of the private sector.
Box 18 - Infrastructure Financing in Nigerian SEZs
4.5.1.2
Key Challenge 2: Legal, Regulatory and Institutional Framework
Another key challenge of SEZ implementation within OIC Member Countries has been issues
related to the legal, regulatory and institutional framework. It is noted that countries such as
Nigeria have implemented SEZ development with either outdated or non-existent frameworks
even though SEZ developments have been launched and made operational. Particular examples
include the Lekki Free Zone and Ogun-Guangdong Zone in Nigeria.
52
52
Zeng, D (2012) SEZs in Africa: Putting the Cart in Front of the Horse?
34
11
2
136
67
50
120
32
31
206
70
95
0
50
100
150
200
250
Ghana
Kenya
Lesotho
Nigeria
Senegal
Tanzania
SEZ Average Country Average
Within the Lekki Free Zone, a concession has been granted by the Lagos State government to
build a sea port near the zone and there are plans to build an airport for the planned Lekki
metropolis. The Ogun-Guangdong zone also faces challenges in terms of off-site roads, power
and gas but a potential investor has agreed to build a power plant for the zone.