Special Economic Zones in the OIC Region:
Learning from Experience
60
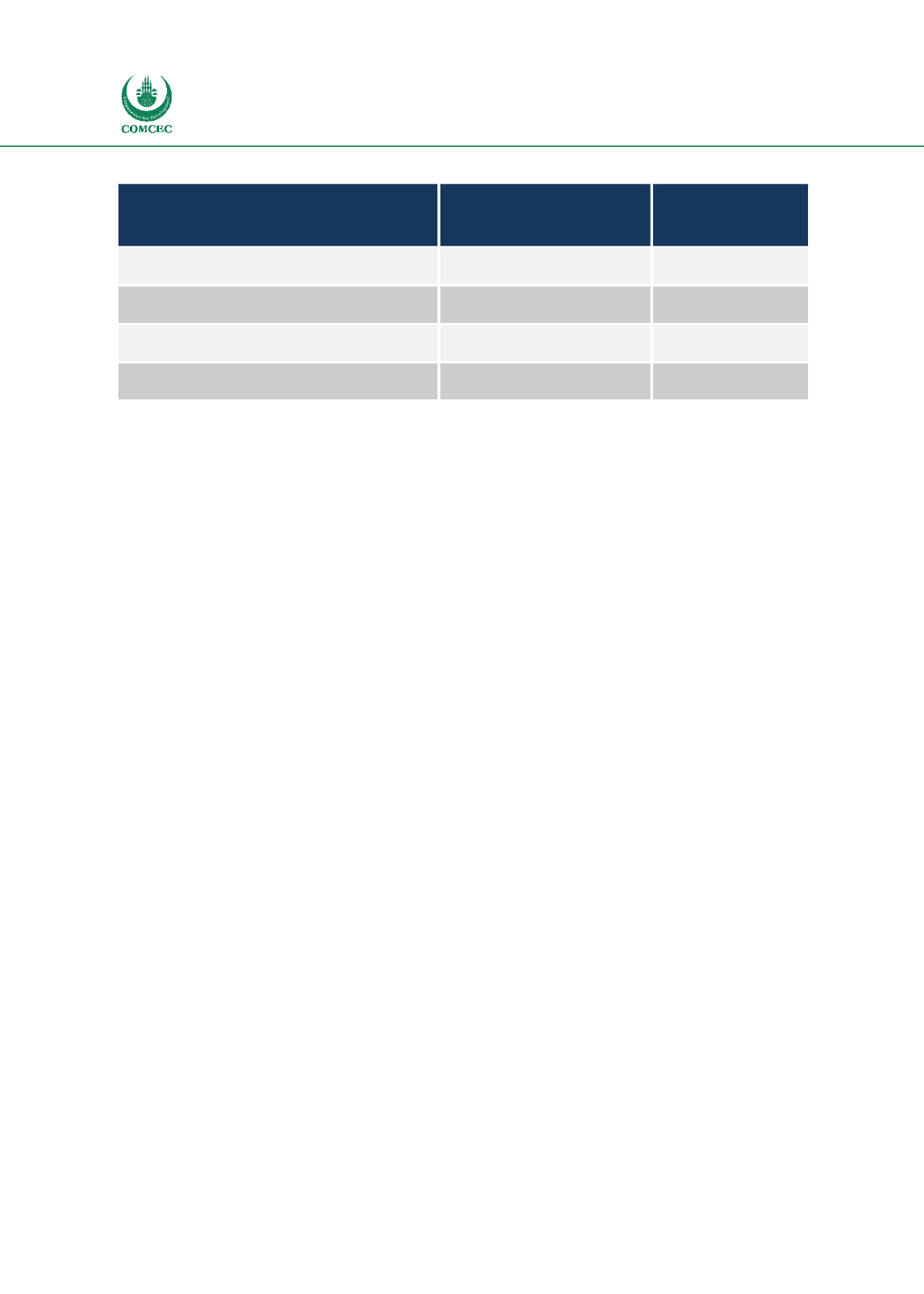
Table 4-5 - Estimates of Direct Employment and Exports in SEZ Regions
Region
Direct Employment
(million)
Exports (US$
million)
Sub-Saharan Africa
1.0
8,605
Asia and Pacific
61.1
510,666
Central and East Europe and Central Asia
1.6
89,666
Middle East and North Africa
1.5
169,459
Source: FIAS (2008)
Key reasons for poor economic performance includes (but is not limited to):
Poor governance and regulatory environment - including ease of doing business.
Poor business environment – including lack of ‘one-stop-shops’;
Inefficient zone management arrangements;
Unreliable utilities infrastructure – including power supply issues;
Poor quality transport infrastructure - including port / airport capacity; and
Some political and social developments – which negatively affects investor confidence.
4.5.1.1
Key Challenge 1: Infrastructure Provision
A particularly acute example of challenges facing SEZs within OIC Countries within SSA is the
provision of high quality infrastructure. This is evident when examining the average monthly
downtime of electricity supply within African SEZs, with a particular focus on Nigeria. It is clear
that Nigeria still suffers from significantly greater disruption due to power shortages than other
OIC Member Countries such as Senegal and other SSA African countries with SEZ development.
Nigeria has however managed to reduce downtime averages compared to area outside of SEZs
by approximately 50%. This is presented below i
n Figure 11.