63
and inevitably they feature on top of the list of barriers faced by Malaysian SMEs. Management problems
of cash flow and the slowing down of markets are also high on the list of challenges. According to an OIC
report innovation and technology adoption together with access to an innovation system are on top of the
list of challenges for Malaysian SMEs. These problems go hand in hand with low commercialisation of
R&D, a lack of know-how and resources and poor technology updates. Human capital development is
relatively low on the list but it is still a problem especially when work force readiness for change and
training issues are raised.
3.5.
Barriers to SME development and exports in OIC countries: a summary
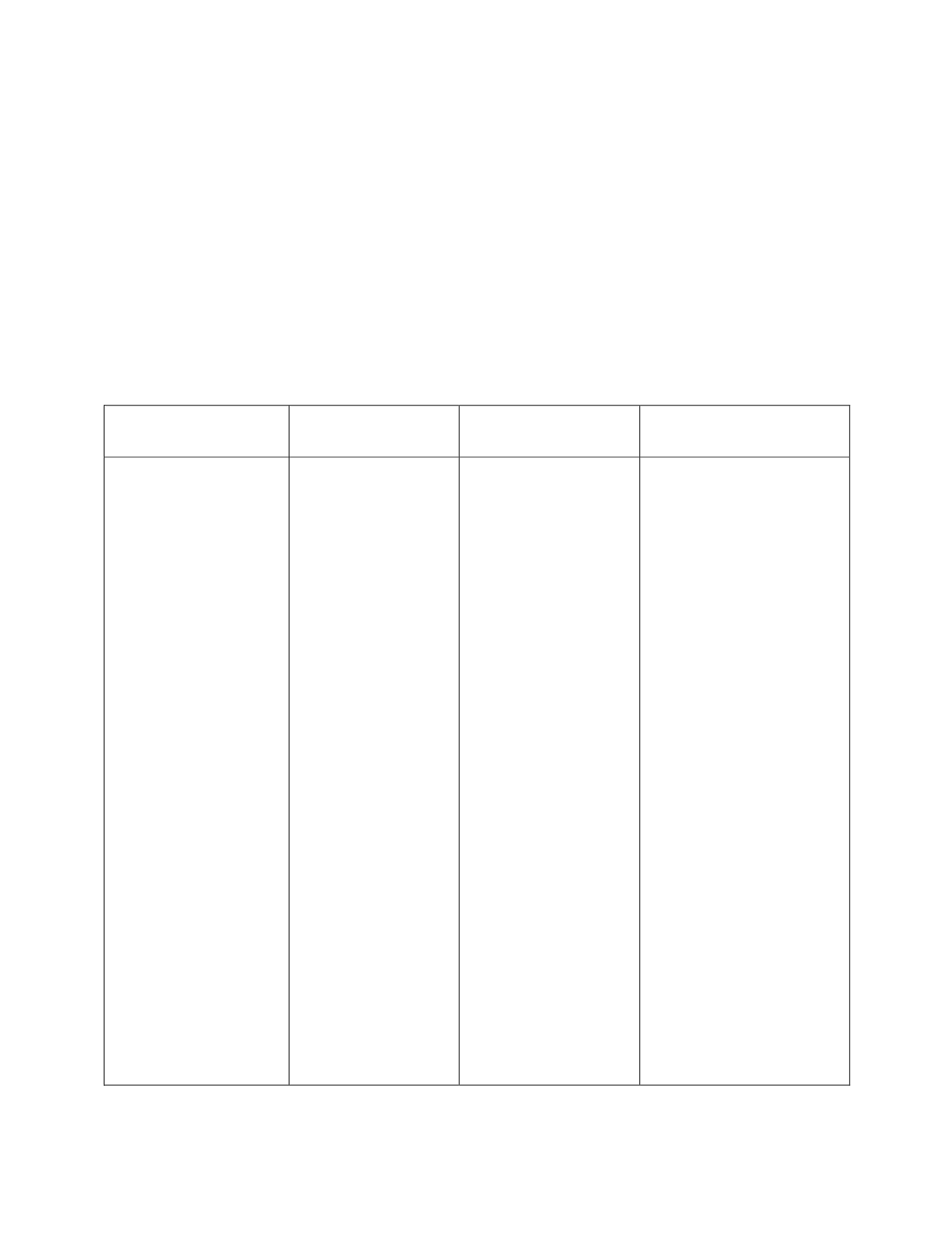
The following table lists a range of issues affecting the ability of MENA country SMEs. These issues are
arranged in four blocks – access to markets, access to technology and innovation; access to finance and
other challenges.
Table 3.12: Obstacles Faced by SMEs in the OIC Countries
Access to Markets
Access to Technology
and Innovation
Access to Finance
Other Challenges, Obstacles
and Problems
Access to Market
Obtaining
reliable
foreign
representation and
maintaining control
over
foreign
middlemen
Identifying
foreign
business
opportunities
Limited information to
locate/analyse
markets
Inability to contact
potential
overseas
customers
Keen competition in
overseas markets
Lack
of
home
government
assistance
Offering satisfactory
prices to customers
Accessing
export
distribution channels
Difficulties
in
enforcing contracts
Lack of knowledge
on foreign market
requirements
Limited
business
development
services, marketing
and branding
Excessive
transportation/
insurance costs
Lack
of
ICT
adoption
Lack
of
R&D
capabilities
Low
level
of
innovation, know-
how and modern
technology
Poor connection
between industry
and universities
Low
level
of
knowledge transfer
between member
countries
Weak
patent
registration
process,
ISO
standards,
certification, and
intellectual
property
rights
(IPR) for SMEs
Weak
infrastructure
of
technology
business
incubation
and
cluster
development
centre
Lack of sustainable
microfinance
programmes
Insufficient
information
dissemination and
transparency
Lack of knowledge
concerning Islamic
and
conventional
financial instruments
Lack of policy and
strategy
of
commercial banks to
deal with SMEs
Lack of banking
capability to deal
with
SME
peculiarities
Lack of access to
the
structural
financial
products
(non-traditional
financial
products)
Lack
of
credit
guarantee schemes
for SMEs
Lack
of
stock
exchange markets
for SMEs
Inadequate
implementation
of
coherent
fiscal
policies for SMEs
Weak business angels
networks
Insufficient
SME
database
Cumbersome
bureaucratic red tape
Lack of transparency in
input prices for SMEs
Inadequate legal and
regulatory framework for
supporting SMEs
Insufficient institutional
support
Lack of bankable projects
Limited capacity building
and training services
available to SMEs
Insufficient public-private
partnership
Lack
of
managerial
capabilities and skills
Lack of promotion and
awareness programs on
the importance of SMEs
on the national economy
Source: COMEC (2012)