Reducing On-Farm Food Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
66
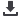
Table 3.9: Production Cost for Peanuts in Azove on One Quanti (400 m2) in FCFA
Activity (1 Quanti/400 m
2
)
Cost(FCFA)
Purchase of Seeds
600
Weeding
600
Soil preparation
500
Planting
400
Weeding
600
Fertilization (NPK)
835
Lifting/Harvest
350
Shelling
400
Transport
350
Total Cost of Production
4,635
Source: Site Visit Observations.
Non-dormant varieties of groundnuts are lifted when 2% of the plants show germination, while
dormant varieties are lifted when a brown spot appears inside the pods. In general, maturity is
recognized by the drying out of the shell of the grains and the detachment of the peduncle from
the seed. After lifting, seeds are dried for two to three days to reduce themoisture content before
shelling. These operations are performed by women and children.
Transport from the field to the home or market is done with motorcycles, motorcycle taxi,
bicycles, or walking. The product is transported either in raffia baskets or polyethylene bags
which protect the product well. Rarely are delays observed in the delivery of the product at
home or in the market. Delays are observed if product needs to be transported on market day
or if there is a shortage of taxi-motorbikes. The distances between fields and house producers
or fields to the nearest market varies from three to eight kilometers.
Pods are stripped approximately two to six weeks after harvesting, when the pod water content
stabilizes at around 10%. This operation consists of separating the pods from the vegetative
parts of the plants (vines). In traditional farming systems, manual stripping is the rule, but this
step has also been mechanized.
The sieving operation is generally done on the farm or at the collecting point. The classic sieve
consists of a hexagonal or cylindrical cage made from bars. It allows part of the trash including
sand, straw and broken pods to be eliminated. However, it cannot eliminate pods of other
varieties, empty pods (pops), partially filled or immature pods. This is the most basic cleaning
operation. In traditional culture, manual shelling is practiced and results in high quality beans
and usually performed by women or children.