Promoting Agricultural Value Chains
In the OIC Member Countries
17
The high growth rates of emerging and developing economies therefore put the spotlight
increasingly on regional market development, including intra-regional and South-South
trade.
However, many barriers continue hindering farmers and other value chain actors to
participate more profitably in regional or global trade. Tariff barriers, in particular, tend to
remain higher for agricultural products than for manufactured goods. Other market
interventions and non-tariff barriers, such as phytosanitary measures, further complicate
obtaining market access. Reports confirm that addressing tariff barriers would have
significant pay-offs. For instance, a study by Moise et al. (2013) finds that a decrease of
tariffs by 10 percent would lead to an increase of agricultural trade volume by about 3.7
percent. In light of the negative impact of tariffs on agriculture, trade policy, including
different forms of regional and international cooperation, has been identified as critical in
establishing reliable systems for moving goods.
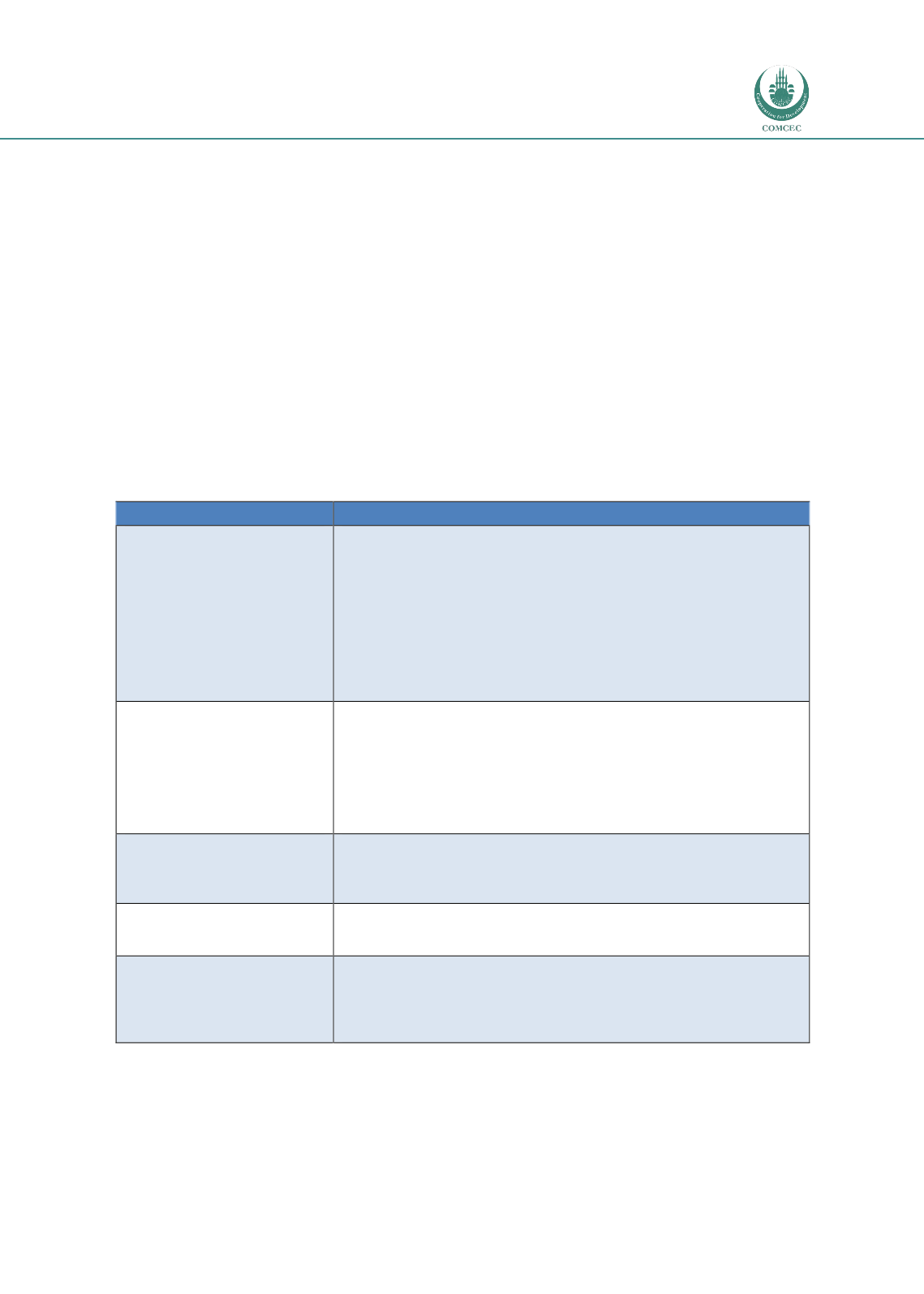
Table 1-1 Framework used to analyse agricultural value chains
Dimension
Indicators
1.
Institutional framework
and public policies
National strategy for agricultural development
Strategic focus on certain commodities/products
Support to chain actors and organisations, e.g. extension, research,
credit facilities, etc.
Specific governmental organisations that develops and promote the
subsector
International programs to support and develop agricultural value
chains
2.
Standards
Quality standards and control
Health & safety standards
Sector codes of conduct
Sustainability standards
Multi-stakeholder initiatives
Government support to help producers comply with international
market requirements, e.g. standards, MRLs, etc.
3.
Infrastructure and logistics
Opportunities and barriers in terms of existing infrastructure
Targeted investments by private and public actors
Electricity and water
Cold chain facilities, transport, processing facilities
4.
Governance and value
chain actors
Actors involved in the value chain
Linkages between actors
Marketing channels and markets
5.
Trade
Exports and imports
Value adding activities
Trade related obstacles (tariff barriers) and opportunities (tax
exemptions; preferential trading areas, free trade agreements)
Non-tariff barriers to trade (e.g. phytosanitary standards, etc.)