The Role of Sukuk in Islamic Capital Markets
23
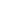
Nonetheless, any generic sukuk issuance would involve the parties listed in Tables 2.2 and 2.3.
While Table 2.2 describes the essential or required parties and their roles, Table 2.3 delineates
some optional parties involved in a sukuk issuance.
Table 2.2: Required Parties in Sukuk Issuances and Their Roles
Parties
Roles and Responsibilities
Issuer
An entity which offers and issues the sukuk; can either be the obligor or an SPV.
Obligor
An entity which needs the funding and is responsible for paying the sukuk holders –
coupon payments and principal amount at redemption.
Originator
An entity which sells the asset(s) to the SPV issuer and receives the proceeds from
the sale of the sukuk. Can also be the obligor or related to the obligor.
Sukuk holder
Owner of the sukuk; can either be the primary subscriber or a secondary investor.
Primary
subscriber
Entity or individual that subscribes to the sukuk offering and is the first holder.
Special-
purpose
vehicle
An entity incorporated in onshore or offshore jurisdictions; this corporate entity is
used to nominally own assets and/or facilitate other aspects of the sukuk issuance
and structure for various purposes, including tax efficiency and asset protection.
Shariah
adviser
The formal authority which approves the sukuk structures in terms of Shariah
compliance; it can be at the institutional level issuing the sukuk and/or at the central
level (e.g. the SAC of the SC).
Regulator
Sovereign approving body; all capital market offerings need to be approved or
exempted by a regulator. Typically, there is a main regulator where the sukuk
is
primarily offered (in the country of the obligor), but international-currency issuances
will need to be approved by the relevant regulators.
Credit
enhancer
A third party (e.g. a government agency, bank or
takaful
company) or a related party
(holding company) that provides a guarantee or some form of credit enhancement.
Investment
bank
A single or small group of investment banks which primarily act the
lead arranger
(arranging the sukuk
offering, advising the issuer/obligor on market conditions, and
coordinating the offering, including marketing); a
rating adviser
(providing advice
on how to achieve an optimal rating); a
book runner
(managing the fundraising,
approaching potential investors, providing guidance on pricing, market conditions
and appetite, and monitoring sukuk
demand and orders); and a
lead manager
(a
significant subscriber of the sukuk
issuance that provides credibility).
Trustee
A professional firm or unit of a bank or law firm which mechanically acts on pre-
agreed instructions; acts and holds the sukuk assets on behalf of the holders.
Facility agent
A professional firm or unit of a bank or law firm which manages the operational
aspects of the sukuk structure, such as the disbursement of the issuance amount and
profit payments to investor accounts. A facility agent can also act as a security
agent/trustee.
Security
agent/trustee
A professional firm or unit of a bank or law firm which manages the assets
securitized/collateralized under the sukuk deal (e.g. holds specific security assets for
the benefit of the holders, realizes/liquidates any mortgage or other collateral in the
event of a default).
Credit rating
agency
A pre-approved professional firm which provides opinions on credit risk and
examines the parties in the transaction and the structure. Credit rating opinions are
issued upon or soon after issuance, and updated throughout the life of the sukuk.
Legal adviser
A law firm which advises on the legal and regulatory requirements (e.g. a legal
opinion on structure and enforceability, and may cover legal due diligence, which
may be a requirement, and guidance on commercial matters.
Source: ISRA (2017)