Improving Transport Project Appraisals
In the Islamic Countries
103
individual projects need to be justified, following a process of project appraisal, as elaborated in
this case study.
This case study benefits from active support and participation from a broad range of
stakeholders in Jordan. Details of relevant experts are presented in Annex 3.
6.2
Legal basis
In Jordan, no legislation is in place that requires project appraisal to be carried out for all
transport projects. However, as illustrated below, for projects that are developed under a
Public-
Private Partnership
(PPP) arrangement,
the PPP Law
stipulates that project appraisal is to be
carried out.
Notwithstanding the fact that there may not be a law, which requires appraisal to be carried out
for all projects, .project appraisal is firmly embedded in the procedures that are applied for new
transport projects in Jordan. It should also be mentioned here that all projects that involve
collaboration with development partners or
International Financing Institutions
(IFIs) – see
below – include project appraisal. Main stakeholders, such as the
Ministry of Transport
(MoT)
and the
Ministry of Public Works and Housing
(MoPWH) confirm that project appraisal is carried
out on structural basis, although the representative of the MoPWH stated that for some projects,
funded though domestic funds, project appraisal may not always be carried out.
Regarding the procedures, a distinction can be made between the following types of projects:
Development projects
, funded by the Government of Jordan.
Projects implemented under a
PPP arrangement
.
Both type of projects require project appraisal, however, the scope of appraisal differs, as
illustrated i
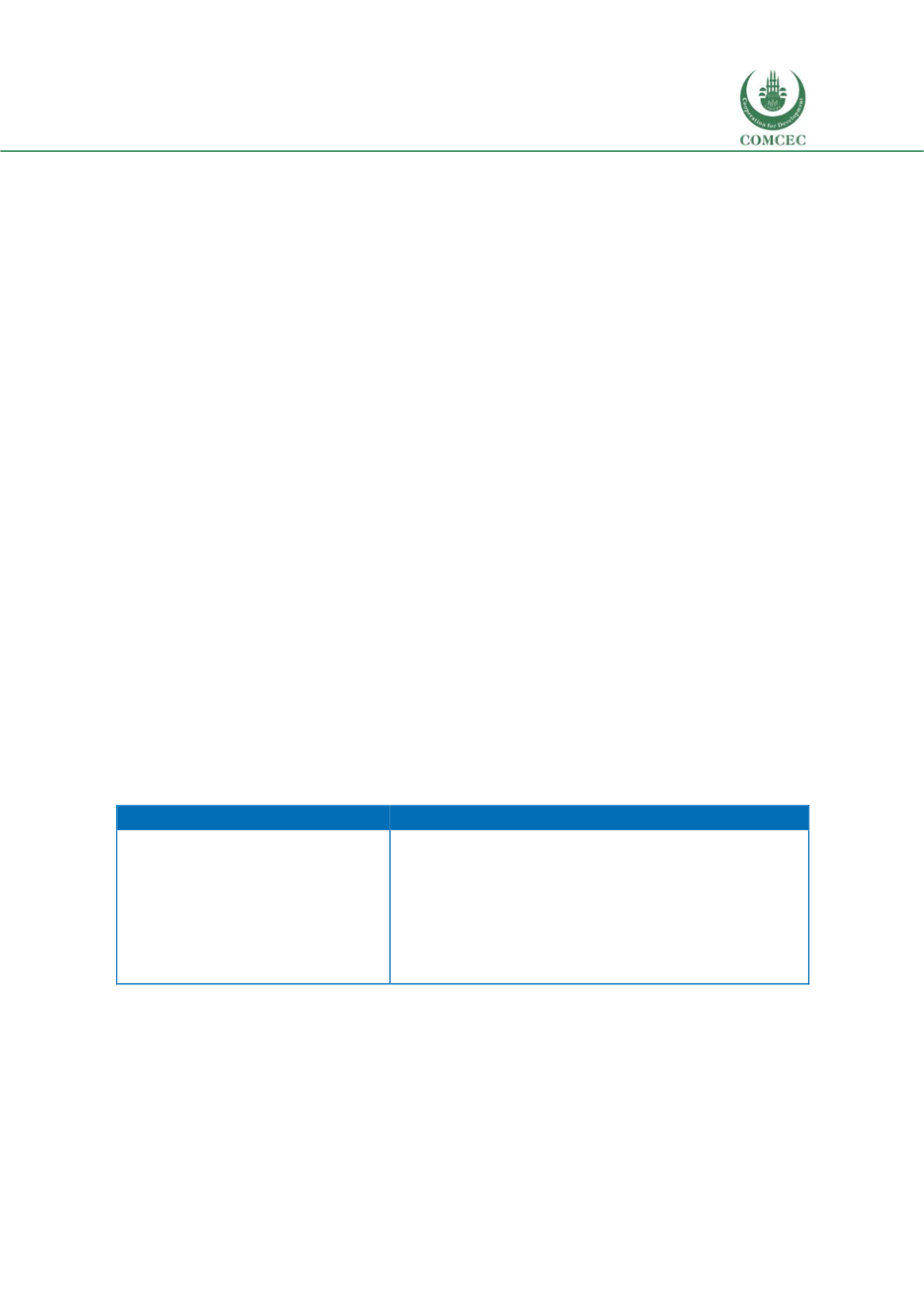
n Table 6.1.Table 6.1: Type of projects and appraisal
Development projects
PPP projects
The focus of development projects is
on socio-economic impact, hence
economic evaluation is applied. Here,
cost and benefits are considered for
society as a whole and the appraisal
seeks social welfare.
The focus of the PPP projects is on bankability of the
projects, and as such financial evaluation is applied
focused on the income and monetary costs associated with
the project, As such, the evaluation considers the project’s
ability to generate income flows that will cover its costs,
resulting in its potential to attract private investors,
whose decisions are assumed to be guided by the objective
of maximum benefit.
Public-Private Partnership Law
The
PPP Law
(Kingdom of Jordan, 2014) describes in Article 7 the establishment of a
PPP Unit
,
undertaking amongst others the following task: to identify the technical requirements that must
be presented by the Government Body for any partnership project. These requirements shall
include the
financial feasibility of the project
, the updated Sustainability Report, and the
cost-
benefit analysis
.