
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
174
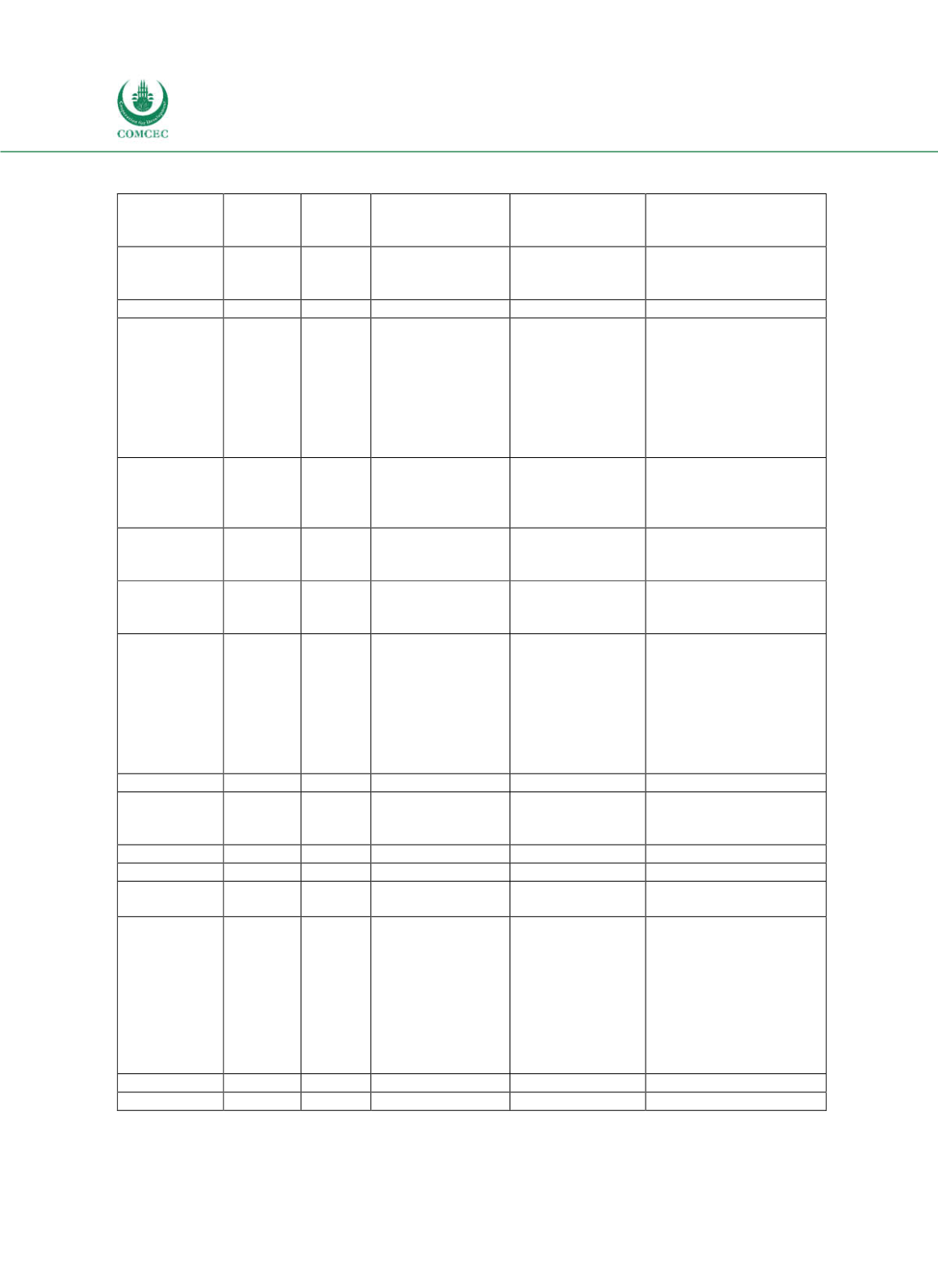
Table 4-13: Comparison of Debt Management Objectives in Case Study Countries
Country
Formal
DeM
strategy
Targets Currency risk
Interest rate risk
Refinancing risk
Gambia
yes
no
Increase ext.
borrowing
(concessional)
Mozambique
yes
no
Togo
yes
no
Extend concessional
and semiconcessional
ext.
borrowing which
generally has higher
maturities;
Target maturities of 310 years for dom.
borrow.
Uganda
yes
yes
Dom. to ext. debt:
40:60;
FX share: Max.
80%
ATR: Min. 10
years
ATM: Min. 3 years;
Debt maturing in 1 year:
15%
Egypt
yes
yes
Dom. to ext. debt:
85:15
Share of fixed
rate debt: 100% ATM: 2.5 years
Debt maturing in 1 year:
Max. 50%
Indonesia
yes
yes
FX share: 39% Share of fixed
rate debt: 89% ATM: 9 years;
Debt maturing in 3
years: 22%
Nigeria
yes
yes
Dom. to ext. debt:
60:40;
Dom. debt mix of
75:25 for long and
shortterm debts.
Increase ext.
borrowing
(concessional)
ATR: Min. 10
years
ATM: Min. 10 years;
Debt maturing in 1 year:
Max. 20%
Sudan
no
no
Albania
yes
FX proportion:
5055%
ATR: Min.
3
years
ATM: Min. 4.7 years;
Debt maturing in 1 year:
Max. 26%
Iran
no
no
Kazakhstan
yes
no
Lebanon
yes
yes
Increased ext.
borrowing
ATR: Min. 4.3
years
ATM: Min. 4.3 years
Turkey
yes
yes*
Make borrowing
mainly in TL
Fixed rate TL
instruments as
major source of
dom.
cash
borrowing;
Decrease share
of
debt with
interest
rate
refixing < 1 year
Increase average
maturity of dom. cash
borrowing;
Decrease share of debt
maturing within 12
months.
Oman
no
no
Saudi Arabia
no
no
Note: * not published; ATM = Average Time to Maturity; ATR = Average Time to Refixing.
Sources: Public debt management strategies, ifo Debt Management Survey (2016).
















