COMCEC Poverty Outlook 2016:
Human Development in OIC
39
ANNEXES
Annex 1: The Widely Used Non-Monetary Poverty Indices
Human Development Index
Human development approach relies on a view that poverty is a multidimensional
phenomenon. This perspective is inspired by Amartya Sen’s
25
notion of well-being and
poverty. Within the context of human development in order to investigate development by
assuming that it is something beyond income and economic growth rates of countries the
UNDP calculates a Human Development Index (HDI).
26
The HDI defines people as "the real
wealth of a nation"
27
and posits
health
,
knowledge
and
income
as three basic aspects of human
measures for development, and calculates a country's average achievements in these areas. In
conclusion, the HDI sees poverty in terms of human poverty and defines it as a lack of income,
education and health.
28
The HDI utilizes four indicators, namely GNI per capita, mean years of schooling, expected
years of schooling and life expectancy at birth, under three dimensions
(Figure 25). When
being calculated the index, minimum and maximum values are set in order to transform the
indicators into indices between 0 and 1. The HDI is calculated by taking the geometric mean of
the three dimension indices.
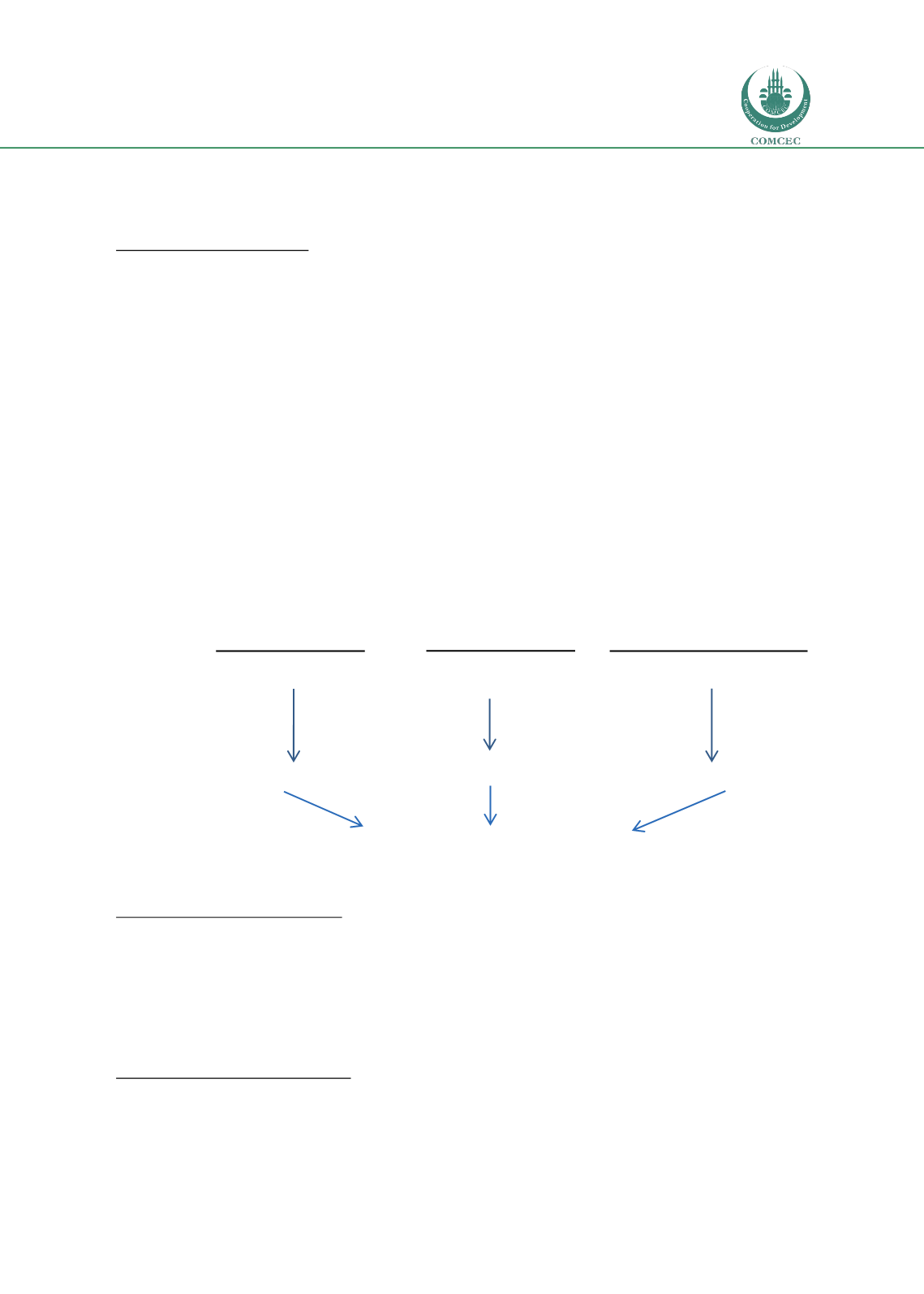
Figure 25: Dimensions of the HDI
DIMENSIONS
Long and healthy life Knowledge
A decent standard of living
INDICATORS
Life expectancy at birth
Mean years of
schooling
Expected years
of schooling
GNI per capita (PPP US$)
DIMENSION
INDEX
Life expectancy index
Education index
GNI index
Human Development Index
(HDI)
Source: The UNDP, 2015.
Multidimensional Poverty Index
Within the context of human development thinking, in addition to HDI, the UNDP have started
to calculate MPI, in order to measure poverty in a much broader context, since 2010. The MPI
considers multiple deprivations of the population and their overlap by utilizing the dimensions
of health, education and standard of living
(Figure 26). While the health and education
dimensions are similar to the dimensions of HDI, but use different indicators, the standard of
25
Sen 1987 quoted in Haughton and Khandker 2009, p.2.
26
Klugmanet.al.2011, p.250; Sagar and Najam 1998, p.251
27
The UNDP 1990, p.9.
28
The UNDP 1990, p.63.