COMCEC Poverty Outlook 2017
28
The lower middle income group has life expectancy, expected and mean years of schooling
values that are very close to OIC average. For high income countries, all the parameters except
expected and mean years of schooling have values that are remarkably higher than upper-
middle income group. However, the mean years of schooling is only 0.4 years higher than that
of upper-middle income this group. Probably, it is mean years of schooling that causes such a
high difference between HDI and GNI rank for high income group.
2.2.2.
Evaluation of Human Development Categories for OIC Member States
In HDR’s, the countries are grouped according to their HDI value. From the first HDR (1990)
until 2009, there were three categories, namely “low”, “medium” and “high” human
development. However, this changed in HDR 2009 and a “very high” human development
category was added to the existing three categories. For this reason, the distribution of OIC
member states within these categories are given in two different tables (se
e Table 6an
d Table 9 ).
In 1990, only 38 OIC member states were included in the HDR. Of these, 22 were exhibiting low
human development, 14 were in medium human development category and only 2 countries in
the high human development category. In 2000, the number of OIC member states covered by
HDR was increased to 54. More than half (29) of these countries were in the medium
development category and 5 were in high development category. The share of these two groups
increased significantly compared to 1990. In 2008, the number of OIC member states remained
at its 2000 level. However, the share of medium and high development categories rose further
to 59 percent and 19 percent respectively.
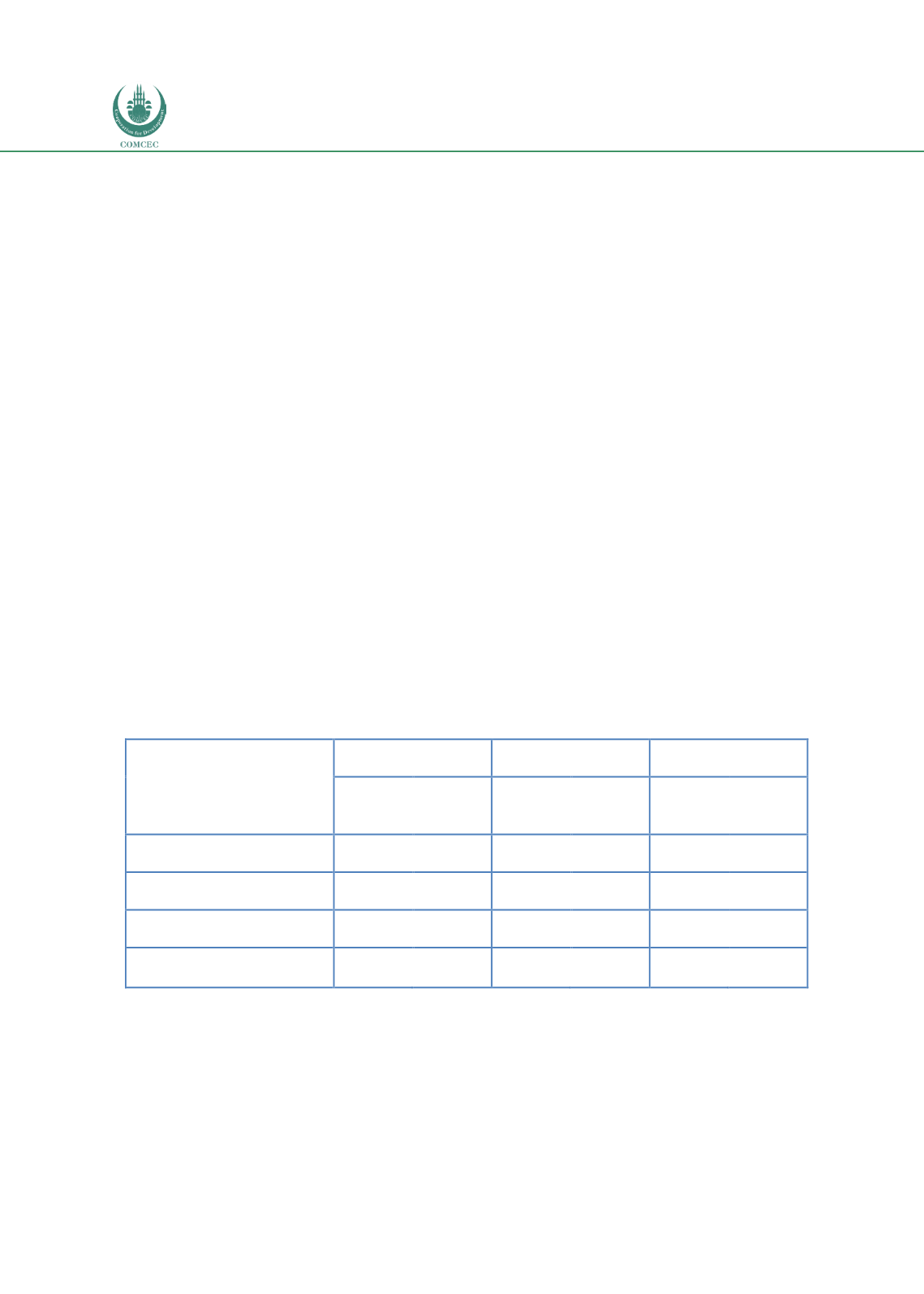
Table 6: OIC Member States by human development level, 1990, 2000 and 2008
HDI Category
1990
2000
2008
# of
Countries
%
# of
Countries
%
# of
Countries
%
Low Human Development
22
58
20
37
12
22
Medium Human Development
14
37
29
54
32
59
High Human Development
2
5
5
9
10
19
Total
38
100
54
100
54
100
Source: Own calculations from corresponding years’ HDR.
Note: The methodology of HDI has evolved over time. Therefore, the HDI values and hence categories are not
fully comparable over time.
Table 7and
Table 8 can be interpreted as transition matrices. According to
Table 7,out of 21
OIC member states which were placed in low development category in 1990, 18 ended up in the
same category in 2000 and 3 climbed to mediumdevelopment category. There was no transition
frommediumdevelopment category neither downwards nor upwards. For two countries in high