COMCEC Transport and Communications
Outlook 2016
52
In addition to increase in the number of internet users, types and nature of online activities are
also continuously changing. New technology and applications such as online video streaming,
voice over IP, machine to machine communication and telecommunication trends like
convergence result in increased data usage and higher speed requirements. These
developments eventually increase the demand for bandwidth, which represents the
transmission capacity of a telecommunication device or system, i.e. the amount of data that can
be transformed in a given time period. This increasing bandwidth demand creates the need for
“broadband” internet.
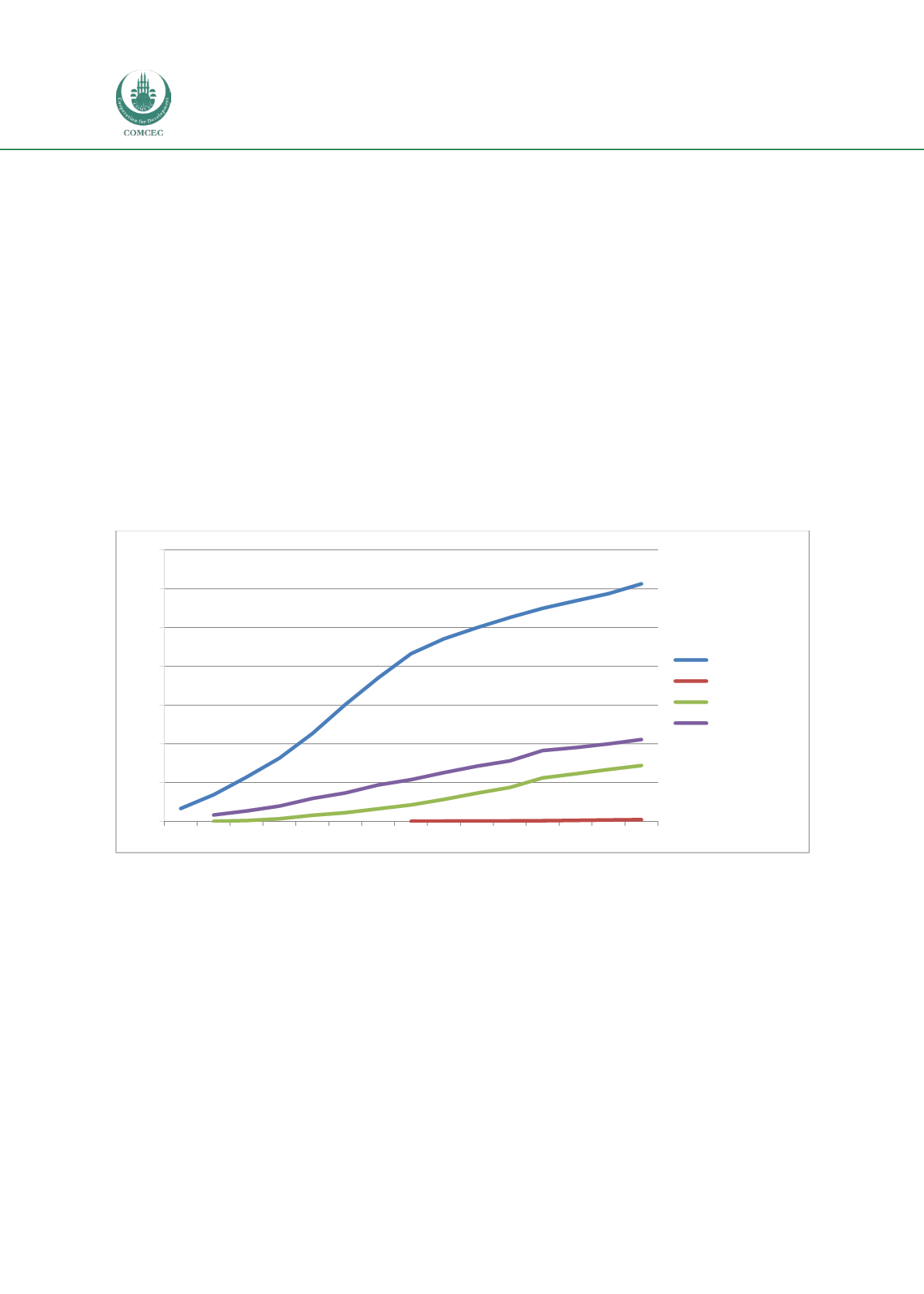
As Figure 29 illustrates, fixed broadband subscriptions have been rapidly increasing, especially
in high income countries. Global average of fixed broadband subscriptions per 100 people was
about 11 in 2014 while the same figure was only 3 ten years ago. On the other hand, while
average broadband subscriptions per 100 people exceeded 30 percent in high income countries,
it is just 0.2 percent in low income countries.
Figure 29: Fixed broadband subscriptions (per 100 people) (2000-2014)
Source: World Bank
Internet usage throughout the globe has been rapidly increasing. While the total number of
internet users in the world was about 1 billion in 2005, it reached 3.2 billion in 2015. Internet
usage rate reached 83 percent in 2014 in high income countries, while it was 35 and 6.5 percent
for middle and lower income countries respectively. Similar to fixed broadband subscriptions,
there is a huge difference between high and low income countries in terms of internet usage and
this gap is not diminishing, if not growing. This divide poses a serious threat of deepening
existing social and economic inequalities.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
High income
Low income
Middle income
World