COMCEC Agriculture Outlook 2016
46
The causes of food losses on-farm period vary according to agricultural commodities.
For instance, such losses in vegetable commodities and products are mainly caused by
diseases, insects, weeds, and rodents, severe weather during planting and inefficient seeding
36
.
Moreover, unavailability of harvest fleets or outdated harvest machineries can also bring about
delayed or deteriorated harvest. Regarding root and tuber losses, in low income countries, the
main reasons are outdated production technologies, disease and pest as well as high
temperatures during the harvest period and little or no access to pre-cooling facilities. On the
other hand, in high income countries, rigorous standards relating to the weight, size shape and
appearance may result to high losses at the farm-level
37
.
Regarding livestock and fisheries products, on-farm food losses mainly refer to death
and diseases before first-stage processing, such as animal death during breeding for bovine
and poultry meat, discards during fishing for fish, and decreased milk production due to dairy
cow diseases for milk
38
.
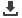
Figure 38. Share of Stages in Value Chain in Food Lost or Wasted by Region
Source: World Resources Institute analysis based on FAO, 2011
Reducing food loss and waste has significant potential benefits for ensuring food
security in the World. With comprehensive strategies for reducing food loss and waste,
countries can increase food availability and alleviate undernourishment and poverty. It has
also environmental benefits with reducing unnecessary greenhouse gas emissions and wasted
water and land.
36
Liu G., 2014
37
FAO, 2014
38
Liu G., 2014
61%
46%
52%
34%
28%
13%
5%
7%
11%
9%
18%
17%
15%
13%
9%
2%
5%
4%
6%
4%
7%
6%
23%
12%
21%
22%
37%
37%
17%
17%
23%
23%
28%
32%
39%
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
90%
100%
North America
and Oceania
Industrialized
Asia
Europe North Africa,
West and
Central Asia
Latin America South and
Southeast Asia
Sub-Saharan
Africa
Percent
Production Handling and Storage Processing Distribution and Market
Consumption