COMCEC Agriculture Outlook 2017
11
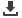
Figure 7. Share of Agricultural Employment in the OIC and World
Source: Annex 9 and 10
The decline in the proportion of agricultural employment can be explained by biological,
chemical, and mechanical advances eliminating many plantation, cultivation and harvesting
task, increasing agricultural productivity, rapid urbanization, and non-farm activities
providing an increasingly important share of rural incomes.
1.5.
Agricultural Trade
This section discusses the change in the aggregate trade of the OIC member countries. Data
used for the aggregates are retrieved from Trade Map which is a customized data repository
tool developed by International Trade Center of UNCTAD/WTO (TRADEMAP). Unless
otherwise is stated, “Total agricultural products trade” covers agricultural and food products
as well as agricultural raw materials (SITC sections 0 (Food and Live Animals), 1(Beverage &
Tobacco), 2(Crude Materials), 4(Animal and Vegetable Oils, Fats and Waxes, excl. 27&28)).
Agricultural commodity trade of the 57 OIC member countries increased considerably in the
last decade up to 2016. Total agricultural trade in the OIC member countries grew by more
than 4 times during this period and reached 329 billion US Dollars in 2016 (Figure 8). In 2016,
total agricultural commodity imports of OIC member countries reached 196 billion US Dollars,
from 42 billion US Dollars in 2001. Correspondingly, total agricultural commodity exports of
OIC member countries was 133 billion US Dollars in 2016 compared to 28 billion US Dollars in
2001.
52,8
48,0
45,5
42,1
38,5
35,8
48,2
46,3
39,6
36,0
32,4
29,5
25
30
35
40
45
50
55
1990
1995
2000
2005
2010
2015
Percentage
Share of Agricultural Employment in the OIC
Share of Agricultural Employment in the World