
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
20
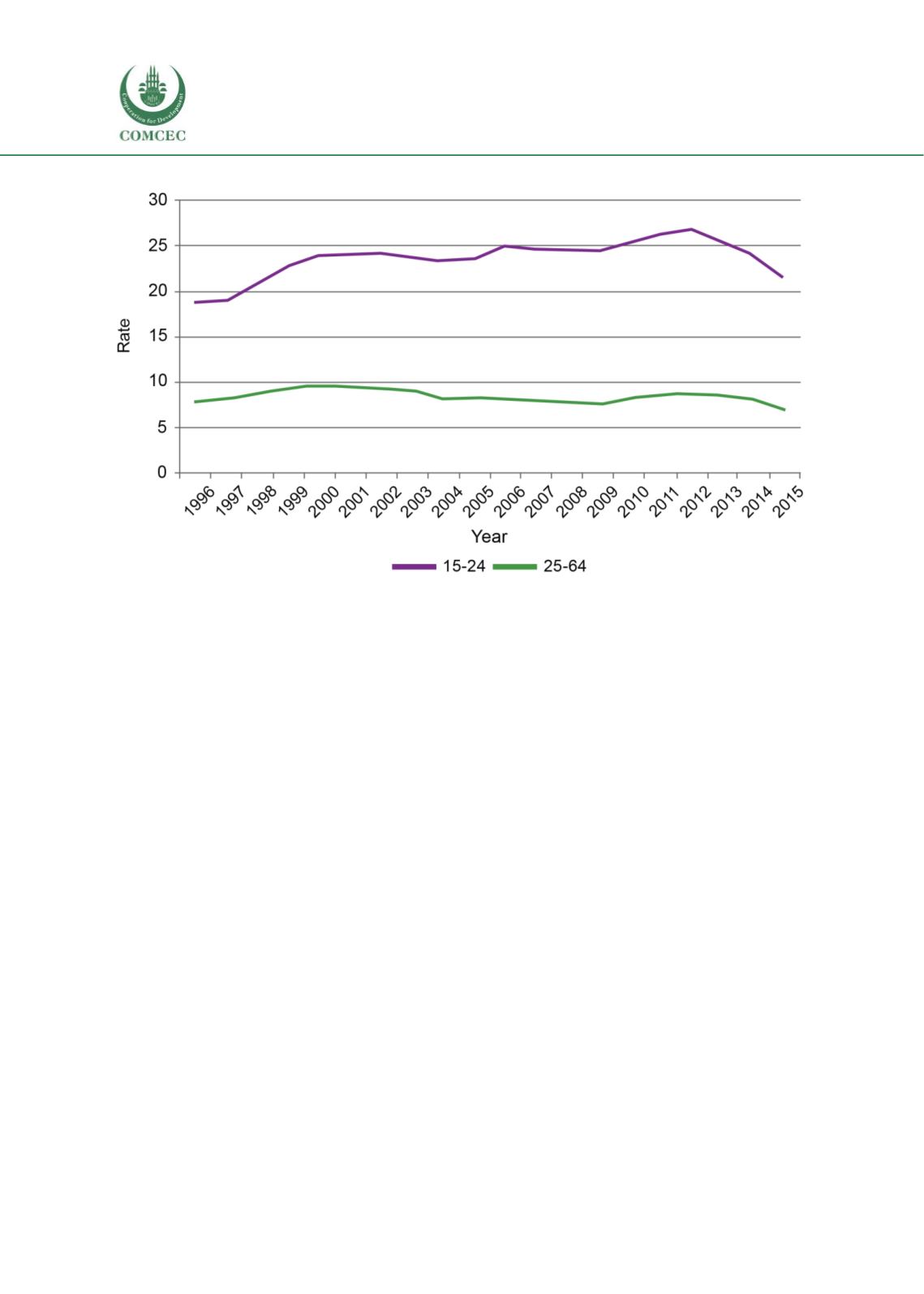
Figure 1.5: Rates of participation in VET by age, 1996-2015 (%)
Note: The rate is expressed as students as a proportion of the 15 to 64 -year old-population
Source: NCVER Historical time series of government funded VET 1996-2015
It is important to mention that, younger people with age below25 years enter in VET system at
higher rates than the aged people who are over 25 years old (Atkinson & Stanwick, 2016).
1.4.6. Competence-Based Training (CBT) in VET
Competence-based training (CBT) refers to the way of describing the capabilities of employees
to perform in a certain way in organizations.
Competency-based skill training is based on the
notion of employment-related competencies which is ‘seen as a human capital and a source of
economic growth’(Marginson, 1993). CBThas reached a global benchmark for TVET curriculum
which represents a more explicit human capital model (ILO, 2005). It is now widely being
utilised in many developed and developing countries (Harris, Guthrie, Hobart, & Lundberg,
1995; Winterton, Delamare-LeDeist, & Stringfellow, 2006). In CBT, trainees are assessedagainst
industry-oriented standards and hence it confirms the relationship between training and
practical work which help relate TVET to the labour market.
Education for all is still far from reality and yet the twenty-first century is highly characterized
by knowledge, information and changing technologies. Individualsmust have capacities of being
employed, obtain decent work, and increase their earnings to have improved living conditions
(especially in developing countries). This can easily be achieved through VET whichwill not only
contribute to economic and social development but also to sustainable development(Maclean&
Wilson, 2009).
1.5. Assessment Techniques of Measuring the Performance of Vocational Education
As many students graduate fromvocational institutions to join the job market, a question arises
as of how to assess their performance and the performance of their institution. Students need to
be evaluated on the basis of institutional level and national or state level irrespective of their
















