
Skills Development: Vocational Education
in the Islamic Countries
191
THEME 2:
How appropriate skill acquisition has led to the reduction of poverty
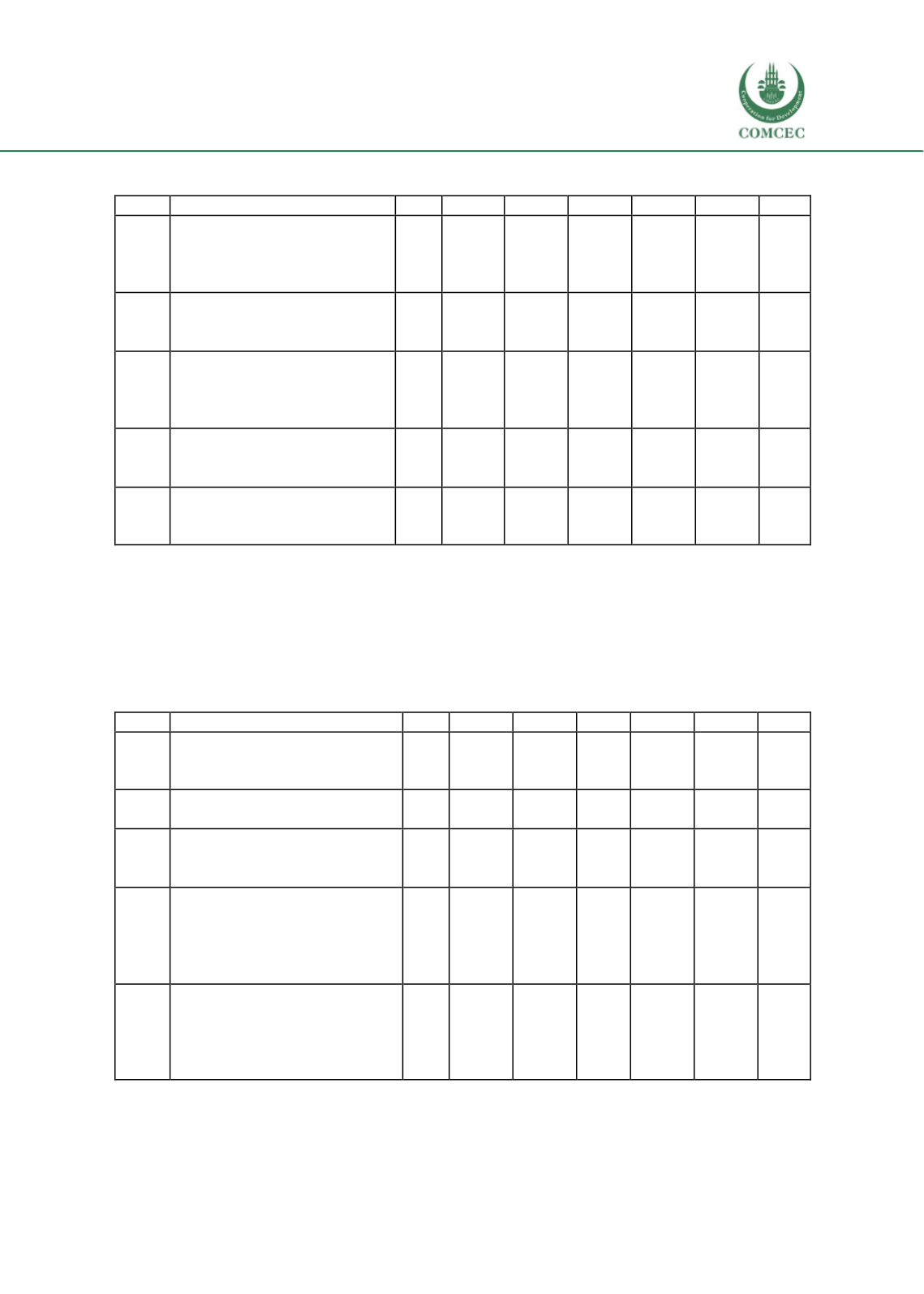
S/No ITEMS
T
SA
A
N
DA
SDA
X
1
Integration of basic skills in
school level provides young
people necessary skills to get
an occupation for living
210 101
48.1%
99
47.1%
6
2.9%
2
1%
2
1%
4.40
4
Country has provision to
attract poor people towards
skilled training
208 26
12.5%
113
54.3%
23
11.1%
39
18.8%
7
3.4%
3.51
5
There is a lack of link
between skill development
and industry practice (thus
leading to low employments)
209 38
18.2%
69
33%
12
5.7%
60
28.7%
30
14.4%
3.12
6
The government provides
free skills for students from
poor families
207 23
11.1%
38
18.4%
19
9.2%
77
37.2%
50
24.2%
2.55
7
The government and private
sectors have created a
number of job provisions
208 59
28.4%
80
38.5%
11
5.3%
42
20.2%
16
7.7%
3.60
Is there any other effort for skill training towards poverty reduction or attracting poor students
towards skilled training?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………
THEME 3:
The success and failure with regards to relationship between the vocational education
and the poverty in the context of Uganda
S/No ITEMS
T
SA
A
N
DA
SDA
X
1
People have negative attitudes
towards enrolling TVET
sectors
209 89
42.6%
88
42.1%
10
4.8%
19
9.1%
9
1.4%
4.18
3
Skill training has reduced
poverty levels in the country
207 55
26.6%
92
44.4%
18
8.7%
33
16.9%
7
3.4%
3.72
4
Due to gender inequality, the
majority of women have not
been trained
206 39
18.9%
63
30.6%
8
3.9%
48
23.3%
48
23.3%
2.99
5
TVET Institutions have
organized industrial
attachments (internship) for
enhancing skills among the
students
208 95
45.7%
95
45.7%
2
1%
8
3.8%
8
3.8%
4.25
7
Industries provide feedback to
us (TVET institutions) that
graduates are unable to meet
the current industrial
requirement.
207 42
20.3%
116
56%
15
7.2%
20
9.7%
14
6.8%
3.73
















