Improving Customs Transit Systems
In the Islamic Countries
14
goods. Some countries are prescribing the route and time for transit in order to avoid checking
along the transit route.
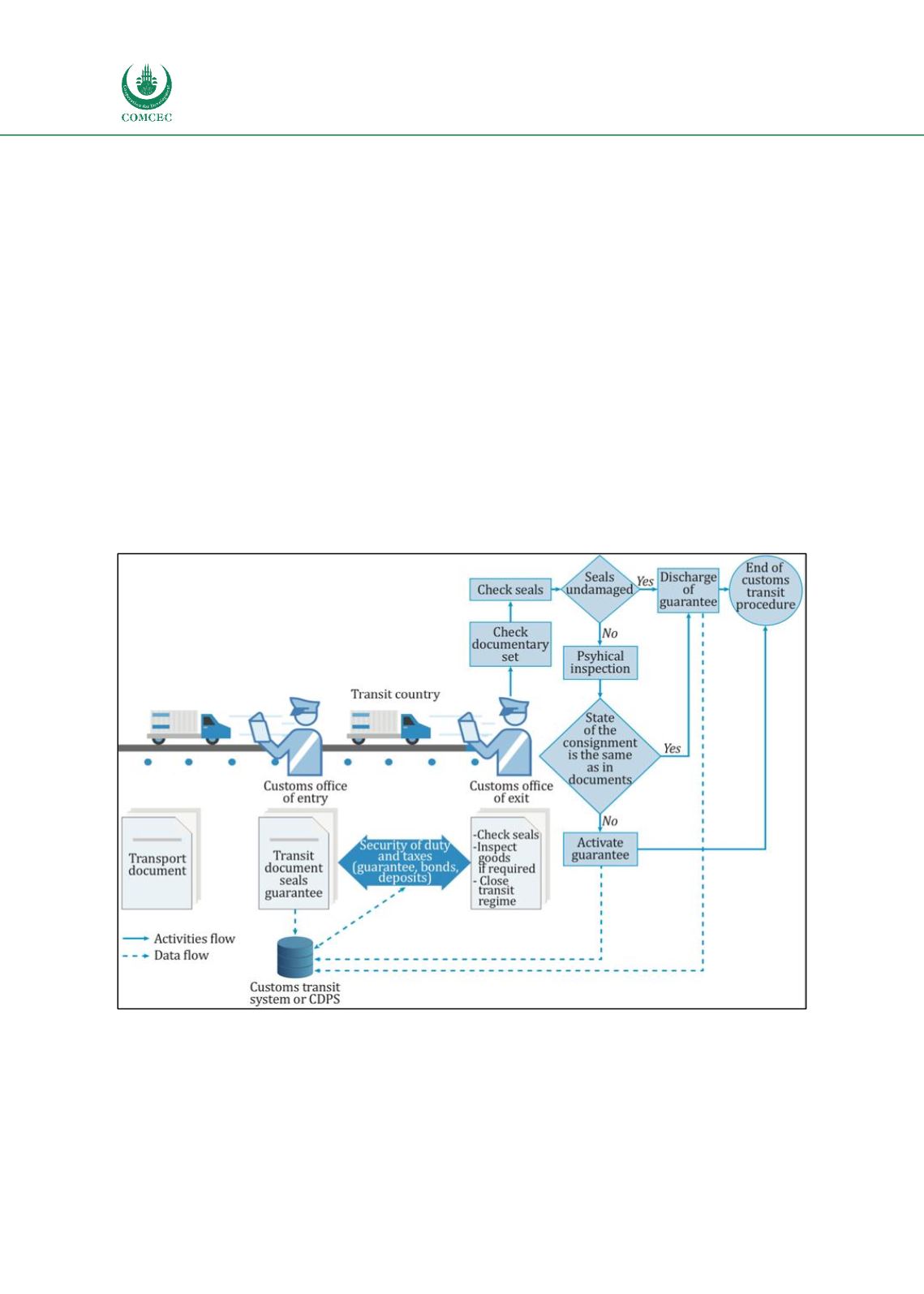
Customs office of exit
- When transit goods come at the customs office of exit or an inland
customs office, customs officer checks the documents, the seals and if the seals are undamaged,
it will release the guarantee, thus completing the transit procedure. If there is a problem with
the seals, or with the documentary check, the customs office can decide to inspect the goods
physically. If the state of the goods is the same as they are according to the documents, it will
discharge the guarantee and finish the transit procedure. However, if the inspection results in
an altered state of the transit goods, the customs office of exit will activate the guarantee and
charge for the duties and other taxes. Customs transit procedures require the exchange of
information between at least three locations: the customs office of entry where the transit
procedure is initiated, the customs office of exit where the transit procedure is closing, and the
guarantor for validation and discharging the guarantee.
Figure 1: Typical customs transit procedure
Source: Author’s own compilation
These procedures, in large part, will be based on customs offices and their infrastructures such
as ICT, area for inspection and non-intrusive equipment.