FACILITATING INTRA-OIC TRADE:
Improving the Efficiency of the Customs Procedures in the OIC Member States
80
Transit trade is also facing obstacles. Therefore international trade of the landlocked
Member States is negatively affected due to these underdeveloped transit regimes.
Escort requirements and high transit fees and duties are among the most important
obstacles faced in some of the transit countries. Some of the countries began using GPS
Systems replacing escorts which had positive impact on transit trade.
Advanced rulings is not implemented by most of the Customs Administrations.
3.2.
I
NTERNATIONAL
C
OOPERATION IN THE
A
REA OF
C
USTOMS
The vital role of international cooperation in the area of customs has been recognized by
many Member States during the last decade. Member States have increased their
bilateral cooperation, initiated regional programs and actively participated in the
multilateral negotiations. These efforts have contributed to their reform process.
However, there are still some Member States, which need to spare more efforts to
benefit from the international cooperation to support increasing the efficiency of the
customs procedures.
-Multilateral Cooperation
Harmonization of trade policies, especially the customs formalities with the modern
standards is a guiding principle for many countries in their reform process. These
standards have been developed with the contribution of many countries under the
umbrella of relevant international institutions e.g. WCO, UNECE, WTO. Under these
international organizations several international conventions have been developed in the
area of trade facilitation which envisage increasing the efficiency of the customs
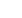
procedures. Figure 9 illustrates the number of Member States which have acceded to the
relevant international conventions in the area of customs.
Unfortunately, some of the Member States have not acceded to most of these
conventions. For example, none of the Member States in Sub-Saharan Africa have
acceded to the TIR Convention and International Convention on the Harmonization of
Frontier Control of Goods. With regards to other conventions, only Mali and Nigeria
have acceded to the İstanbul Convention and four countries from the region have
acceded to the ATA Convention.
Among the 57 Member States, only Turkey has acceded to all of these conventions. On
the other hand, Comoros, Iraq, Palestine and Somalia did not accede any of these
conventions.