Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
120
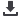
Table 4. 32 Tariffs Set by Gambia for Top 5 Import Products from the OIC Exporters, %
05:
Vegetables,
fruit
41-42-43:
Oils, fats,
waxes
07: Coffee,
tea, cocoa,
spices
08: Feeding
stuff for
animals
11-12:
Beverages,
tobacco
2014
15.7
20.0
4.3
5.5
20.0
2015
16.7
20.0
5.4
5.0
19.8
2016
16.2
20.0
5.3
7.0
19.9
Source: ITC Macmap, CEPII BACI, Eurostat RAMON, UN Comtrade, UN Trade Statistics, and authors’
calculations
Note: Top 5 products are identified considering 3 year average between 2014 and 2016 and ad valorem
equivalent (%) rates are considered for applied tariff rates.
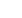
Table 4. 33 Tariffs Set by OIC Countries for Gambia’s Top 5 Export Products, %
03: Fish
02: Dairy
05:
Vegetables,
fruit
08: Feeding
stuff for
animals
06: Sugars
2016
9.0
5.1
14.6
1.5
3.0
Source: ITC Macmap, CEPII BACI, Eurostat RAMON, UN Comtrade, UN Trade Statistics, and authors’
calculations
Note: Top 5 products are identified considering 3 year average between 2014 and 2016 and ad valorem
equivalent (%) rates are considered for applied tariff rates.
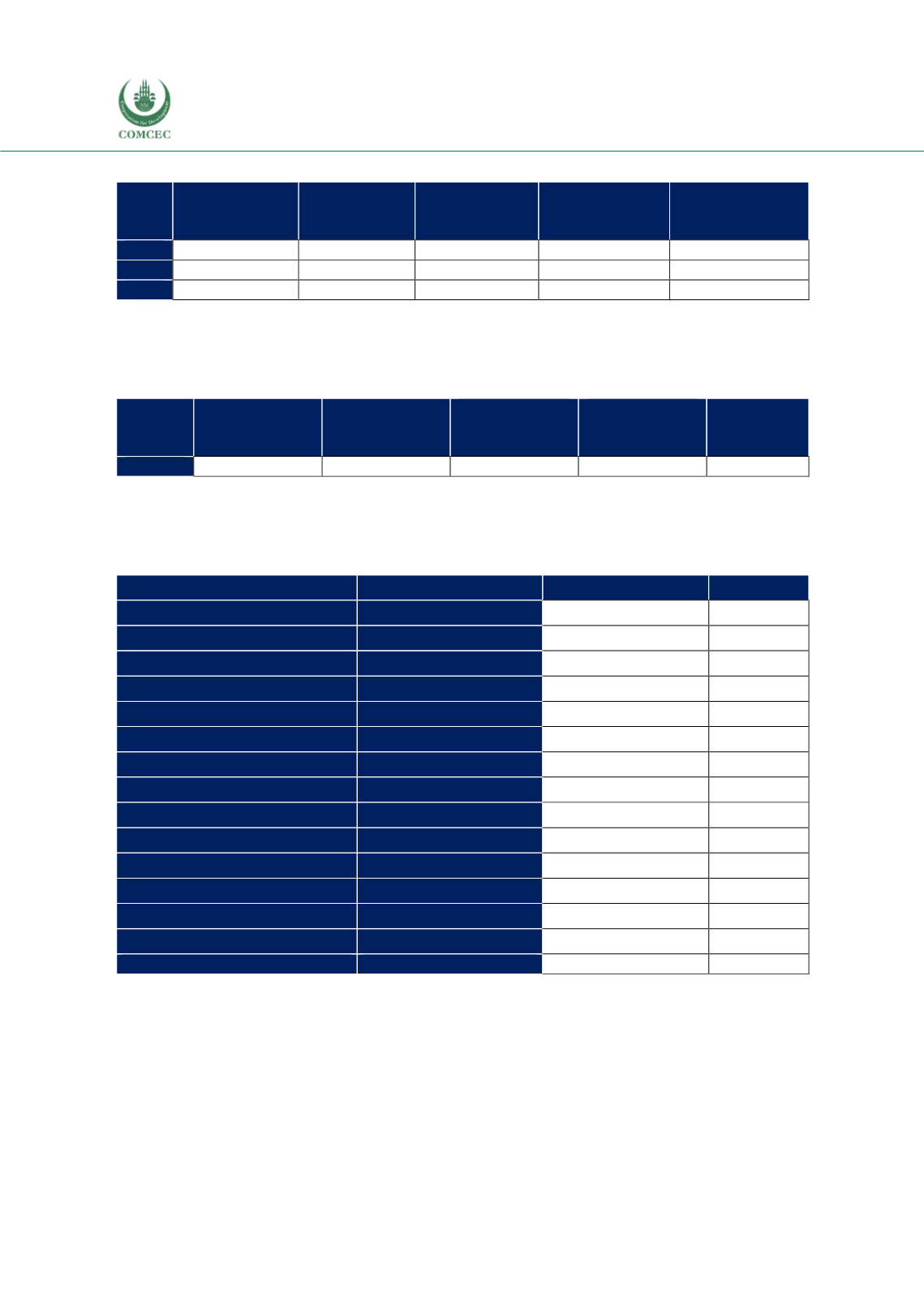
Table 4. 34 NTM Types and NTM Affected Products, Gambia
Sector
NTM Type
Share %
Count
Animal
1 type
8.8
20
Animal
2 types
23.7
54
Animal
3+ types
12.3
28
Animal
No NTMs
55.3
126
Vegetable
1 type
0.7
2
Vegetable
2 types
48.2
145
Vegetable
3+ types
1.0
3
Vegetable
No NTMs
50.2
151
Food Products
1 type
5.2
10
Food Products
2 types
40.4
78
Food Products
3+ types
16.6
32
Food Products
No NTMs
37.8
73
Hides and Skins
1 type
1.5
1
Hides and Skins
No NTMs
98.6
68
Wood
No NTMs
100.0
237
Source: WITS
Animal products, food products and vegetable products are mostly protected through NTMs
where the most common forms of NTMs are SPS, technical barriers and trade related investment
measures. For example, almost all of the import value of animals are protected with SPS and
technical barriers while some animal product items are protected through trade related
investment measures. Majority of food products and vegetable products are protected through
SPS measures where a large fraction of vegetable products are protected with technical barriers
to trade as well (Table 4.34).