Authorized Economic Operator Programs
In the Islamic Countries:
Enhancing Customs-Traders Partnership
45
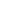
In the OIC Region, 3 countries are in the development stage of an AEO program presented in
Table 3.3. Bangladesh has started the pilot phase as early as 2015. They are still at the
development stage of the program. Côte d’Ivoire has started the pilot phase in 2017. For these
two countries there are no announced launching dates. Bahrain, on the other hand, has
developed the AEO Program and they will launch it in 2018.
Table 3.3. AEO programs under development: names and launch dates
Country
Name of the Program
Current Status
Bahrain
Authorized Economic Operator
Date to be launched 2018
Bangladesh
Authorized Economic Operator
Pilot started in 2015
Côte d’Ivoire
Authorized Economic Operator
Pilot started in 2017
Source: Authors’ compilation using WCO (2018) data.
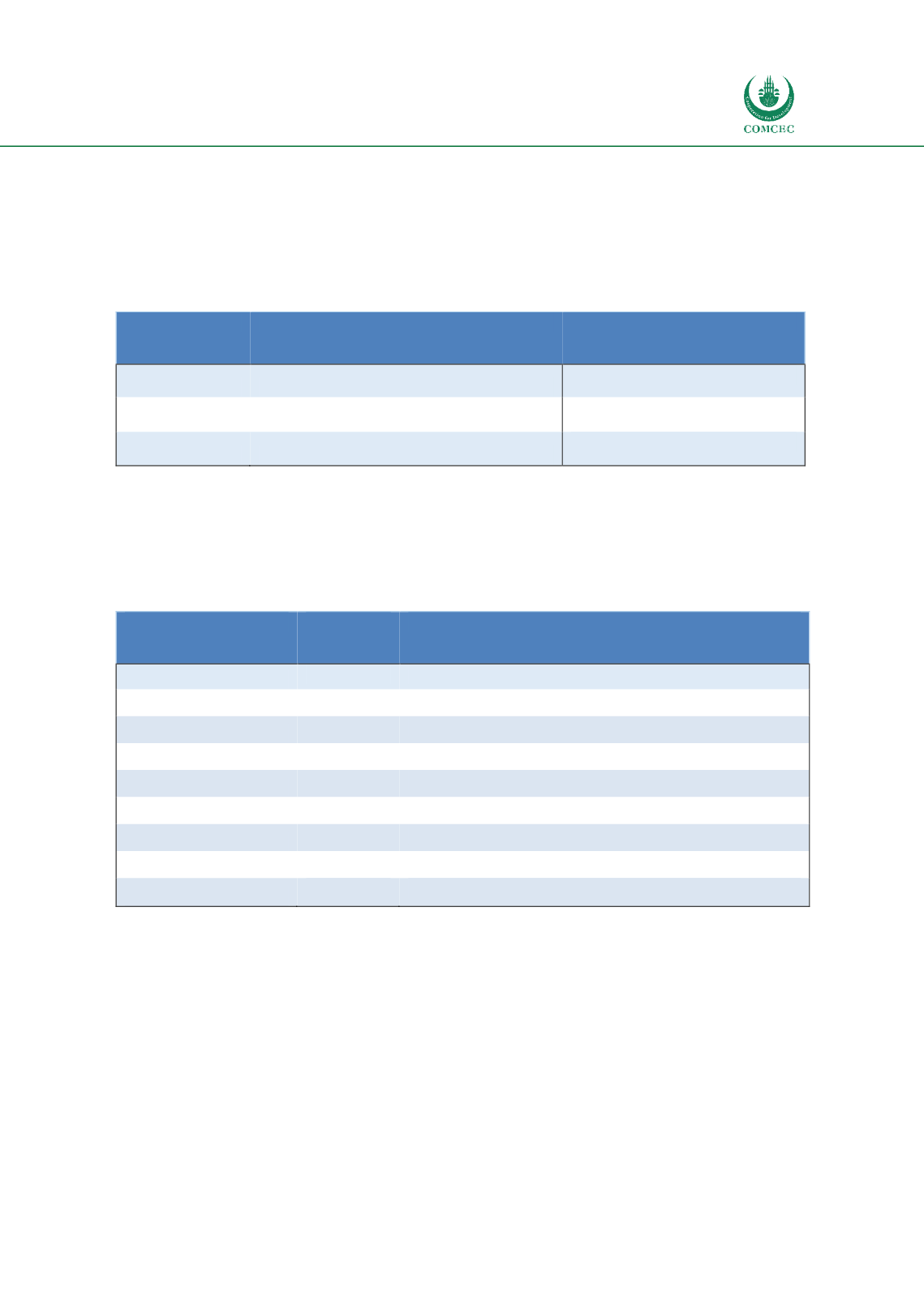
Apart from the AEO program, 9 Customs compliance programs (CCP) are utilized (Table 3.4).
However, it should be noted that CCP does not enable enhanced security in Customs, though
trade facilitations components are the essential parts of CCPs.
Table 3.4. Names and years of CCPs in OIC Countries
Country
Year
CCP
Algeria
2012
Authorized Economic Operator
Cameroon
2011
Performance Operators’ Contracts
Iran
2014
Authorized Economic Operator
Kazakhstan
2013
Authorized Economic Operator
Mozambique
2012
Authorized Economic Operator
Senegal
2012
Privileged Partnership Programme
Sudan
2016
Golden List
Togo
2016
Privileged Partnership Framework
United Arab Emirates
2007
Golden List Programme
Source: Authors’ compilation using WCO (2018) data.
There are 9 OIC countries that initiated a CCP but not an AEO. The names and the launching
years of these CCPs are presented in Table 3.4. In other words, these programs enable trade
facilitation but do not satisfy the security conditions of an AEO program. In 2007, the United
Arab Emirates launched the first CCP in the region. Number of CCPs has started to increase by
2011 following a similar trend with AEOs (Figure 3.5).