11
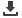
Figure 1.1. AEO and C
ost of
Security C
ompliance
Source: Ahokas and Hintsa (2010).
1.5. Benefits of Mutual Recognition Agreements
MRA is a tool of realizing Customs-to-Customs pillar of the SAFE Framework of WCO. Aigner
(2010) defines the objective of MRA as the recognition of the validation findings and AEO
authorizations of one Customs by the other. With MRAs, both Customs Authorities agree to
provide substantial, comparable and reciprocal benefits/facilitation to the mutually recognized
AEOs. The key point of MRAs is the compatibility of the legislations as well as operational
compatibility of both AEO programs.
The importance of MRAs is their role in the globalization of supply chain security and
compliance standards. On the private sector side, companies that hold the AEO status of a
country that is a part of an MRA will enjoy the same benefits by the other side of the MRA
country. On the Customs side, administrations utilize the information from the partner country
as an input to their own risk analysis, enabling more focused validations and other compliance
benefits.
Benefits of MRAs to the Customs are summarized as follows:
Closer cooperation with third country Customs administrations
More information on supply chains and high risk consignments
Better and more efficient use of scarce resources to high risk transactions
Benefits of the private sector are as follows:
Reduced time and costs due to priority treatment in cross border inspections
Competitiveness enhancement due to the increased predictability and precision in
goods transactions from the company to the territory of the trading partner.
Increased security of the bilateral supply chain due to reduced cargo theft
Reciprocal or comparable compliance benefits