
Facilitating Trade:
Improving Customs Risk Management Systems
In the OIC Member States
85
4.3.1.3
Development of CRM standard operational procedures
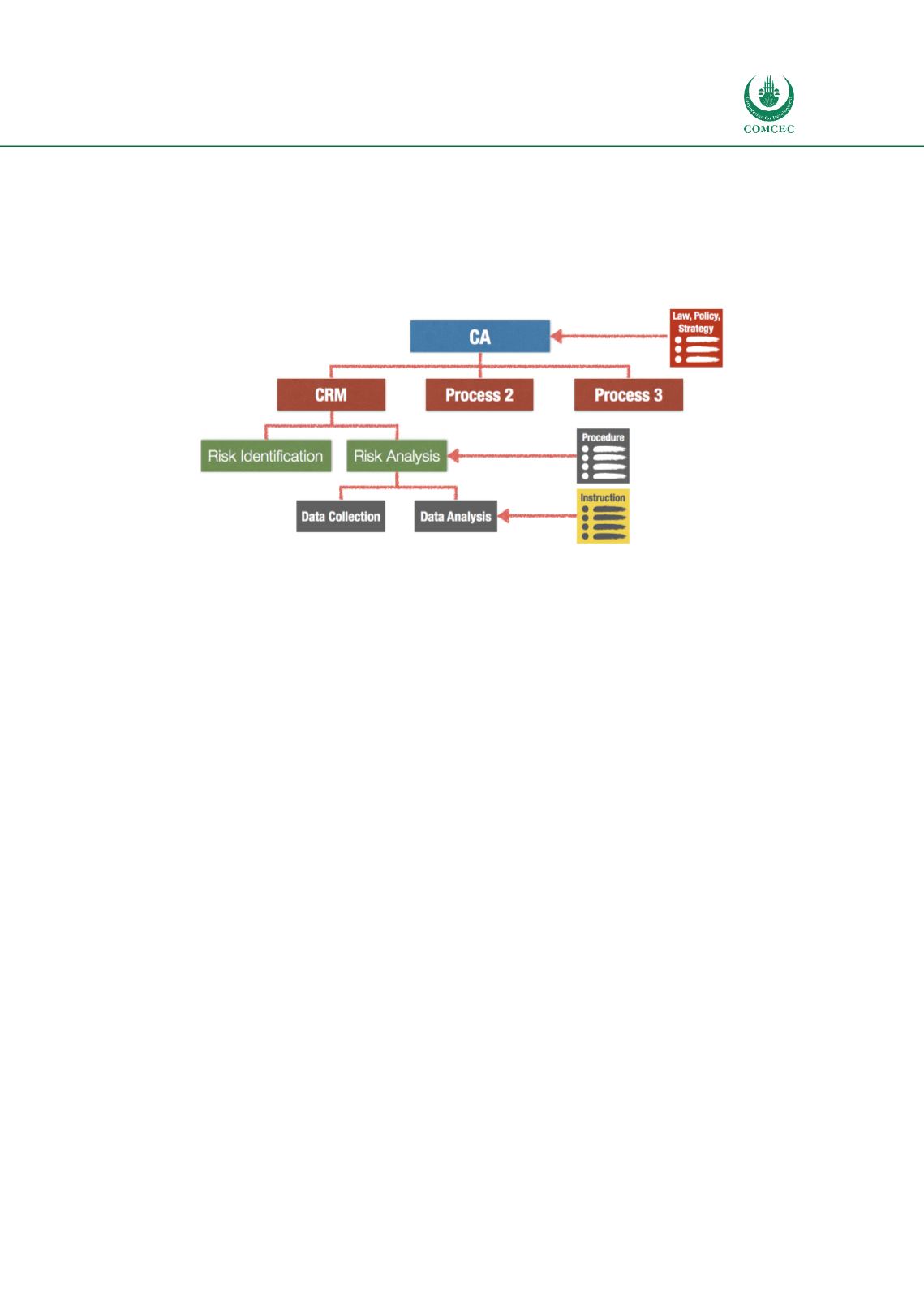
An efficient CRM requires a clear definition of all necessary processes in order to cover all stages
of the CRM cycle. Development of processes needs to start at the top-level, following the legal
environment, policy and, strategy. The processes should be broken down into sub-processes and
procedures following the specifics of the CRM (Figure 26).
Figure 26: Links between policies, processes and SOP
Author’s compilation
According to the responses received from the Survey, 11 of the 16 OIC MS are using the SOP.
There is a no consistency in the responses received, due to the fact that there is a 9 MS with
adopted CRM Policy and 8 with Implementing Regulations. The CRM Policy and Implementing
Regulations are the basis for defining the processes and development of the SOP. Due to the
absence of enhanced SOP and detailed administrative instructions related to CRM, most of the
OIC MS are not able to implement an appropriate risk-based control and feedback/monitoring
accordingly.
The CRM requires changing current processes, redesigning and improving flows to cover the
CRM cycle. To implement these changes effectively, it is very important to perform a business
process analysis on the current processes in detail to recommend improvements. In this way, a
better understanding of the current situation (AS-IS) will be gained, and the recommendations
and simplifications can be proposed for the target situation (TO-BE). Furthermore, business
process analysis allows all parties involved in CRM and LE to gain a better understanding of the
procedural and operational aspects of the CRM. In particular, it informs how business processes
are carried out, how business processes relate to one another, who is responsible for them, what
documents, rules, and regulations are involved, and how this information flows.
4.3.1.4
Risk Management Cycle
The methodology to determine the level of implementation of CRM in OIC MS rests on the seven
stages of the CRM cycle. This allows creating a visual representation of the CRM cycle in OIC MS
CA assessment. The CRM performances for every stage of the CRM cycle is presented on a scale
from 0 to 7, where a value of zero means that a CRM does not apply any of the criteria (CRM
cycle) and a score of 7 means that the CA fully applies the full CRM cycle. The seven stages of the
CRM cycle are recommended by the WCO standards and the reviewed literature. Since the
benchmarks criteria for these stages are uniformly applied between CAs, it is possible to
perform a comparative analysis. The following elements and criteria were used:
Risk Identification;
















